Navigating the Fiery Path: Understanding Lava Flow Maps in Hawaii
Related Articles: Navigating the Fiery Path: Understanding Lava Flow Maps in Hawaii
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Fiery Path: Understanding Lava Flow Maps in Hawaii. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Fiery Path: Understanding Lava Flow Maps in Hawaii
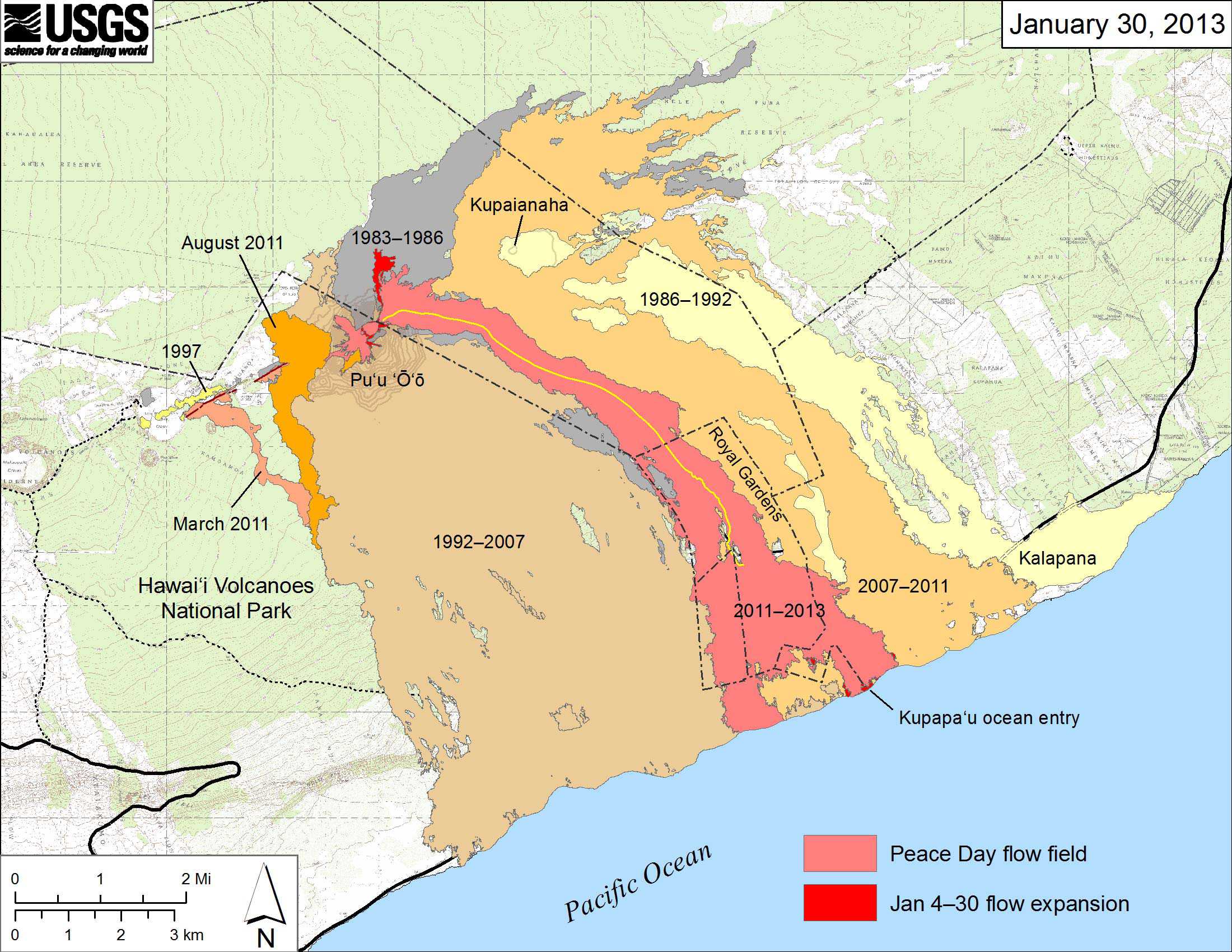
Hawaii, the youngest and most active volcanic island chain in the world, is renowned for its captivating landscapes sculpted by volcanic activity. While the fiery spectacle of lava flows holds a mesmerizing allure, it also poses significant threats to communities and infrastructure. To navigate this dynamic landscape, scientists and emergency responders rely on an invaluable tool: lava flow maps. These maps, meticulously crafted using a combination of geological data, historical records, and real-time monitoring, provide a vital roadmap for understanding and mitigating the risks associated with volcanic eruptions.
Decoding the Lava Flow Map: A Visual Guide to Volcanic Activity
Lava flow maps are essentially visual representations of the potential paths that lava flows could take during an eruption. They are not static, but rather dynamic documents that evolve as volcanic activity unfolds. These maps incorporate a wealth of information, including:
- Past Flow Paths: Historical records of past eruptions are crucial for understanding the typical flow patterns of specific volcanoes. Scientists meticulously analyze the extent and direction of past lava flows, identifying zones of potential future activity.
- Topographic Features: The topography of the landscape plays a significant role in determining the direction of lava flow. Steep slopes can accelerate the flow, while valleys and depressions can act as natural channels, guiding the molten rock.
- Geological Data: Analyzing the composition and properties of the volcanic rock provides insights into the viscosity and speed of lava flows. Highly viscous lava tends to flow slowly and build up thick, dome-like structures, while more fluid lava can flow rapidly and cover vast areas.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Advanced monitoring systems, including ground-based sensors, satellite imagery, and aerial surveys, provide real-time updates on the location, movement, and intensity of lava flows. This data is crucial for refining existing maps and issuing timely warnings to communities.
The Importance of Lava Flow Maps: A Lifeline for Safety and Planning
The significance of lava flow maps extends far beyond academic interest. They serve as essential tools for:
- Hazard Assessment: By analyzing past flow patterns and current volcanic activity, scientists can identify areas most vulnerable to lava flows, allowing for targeted mitigation strategies. This information helps communities understand the risks they face and prepare accordingly.
- Emergency Response Planning: Lava flow maps guide emergency responders during volcanic eruptions. They provide crucial information on evacuation routes, safe zones, and potential hazards, enabling a coordinated and effective response.
- Infrastructure Protection: Critical infrastructure, such as roads, power lines, and communication networks, can be threatened by lava flows. Lava flow maps inform the placement and design of infrastructure, minimizing vulnerability to volcanic hazards.
- Land Use Planning: Understanding the potential impact of future eruptions is vital for sustainable land use planning. Lava flow maps guide development decisions, ensuring that communities are built in areas with minimal risk.
Beyond the Map: A Deeper Dive into Lava Flow Dynamics
While lava flow maps provide a valuable overview of potential hazards, understanding the complex dynamics of lava flows requires further exploration:
- Lava Flow Types: Different types of lava flows exhibit distinct characteristics. Pahoehoe lava, characterized by smooth, ropy surfaces, flows relatively slowly. A’a lava, on the other hand, is characterized by a rough, blocky surface and can flow rapidly.
- Lava Flow Speed: The speed of lava flows varies significantly depending on factors such as viscosity, slope, and eruption intensity. While some flows move at a slow, creeping pace, others can travel at speeds exceeding 10 kilometers per hour.
- Lava Flow Length: The distance that lava flows can travel is influenced by factors such as the volume of erupted material, the slope of the terrain, and the duration of the eruption. Some flows extend for only a few hundred meters, while others can cover tens of kilometers.
- Lava Flow Impacts: The impact of lava flows can be devastating, destroying homes, businesses, and infrastructure. However, the interaction of lava with water can also create spectacular, but potentially dangerous, steam explosions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Lava Flow Maps
Q: How are lava flow maps created?
A: Lava flow maps are created through a multi-faceted approach:
- Field Studies: Geologists meticulously map past lava flow paths, analyzing the composition and age of volcanic rocks.
- Remote Sensing: Satellite imagery and aerial surveys provide valuable data on the current location and movement of lava flows.
- Computer Modeling: Computer models use topographic data, geological information, and real-time monitoring data to simulate the potential paths of lava flows.
Q: Are lava flow maps always accurate?
A: While lava flow maps provide valuable insights, they are not infallible. Volcanic eruptions are inherently unpredictable, and the exact path of a lava flow can be influenced by unforeseen factors.
Q: What should I do if I live in an area threatened by lava flows?
A: It is essential to stay informed about volcanic activity and heed official warnings:
- Develop an Evacuation Plan: Know the designated evacuation routes and have a plan for where you will go if an eruption occurs.
- Prepare a Go-Bag: Keep a bag packed with essential supplies, such as water, food, medication, and important documents, in case of a sudden evacuation.
- Stay Informed: Monitor local news and official sources for updates on volcanic activity.
Tips for Using Lava Flow Maps Effectively
- Understand the Scale: Pay attention to the scale of the map and the units used to measure distance.
- Identify Key Features: Locate key topographic features, such as valleys, ridges, and slopes, to understand how they might influence lava flow direction.
- Interpret Symbols and Colors: Familiarize yourself with the symbols and colors used on the map to represent different types of lava flows and areas of potential hazard.
- Stay Updated: Lava flow maps are dynamic documents that are regularly updated. Always refer to the most recent version available.
Conclusion: A Continuous Journey of Observation and Adaptation
Lava flow maps are powerful tools that help us navigate the complex and dynamic world of volcanic activity. They provide valuable insights into potential hazards, guide emergency response efforts, and inform land use decisions. However, it is crucial to remember that volcanic eruptions are unpredictable events. Ongoing research, continuous monitoring, and a proactive approach to hazard mitigation are essential for ensuring the safety and well-being of communities living in volcanic regions.



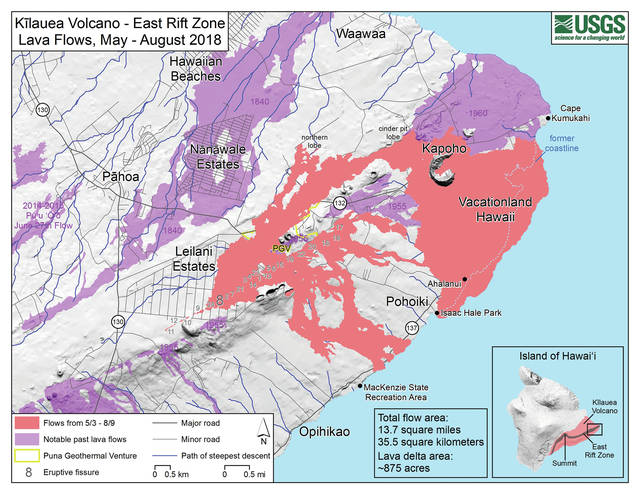


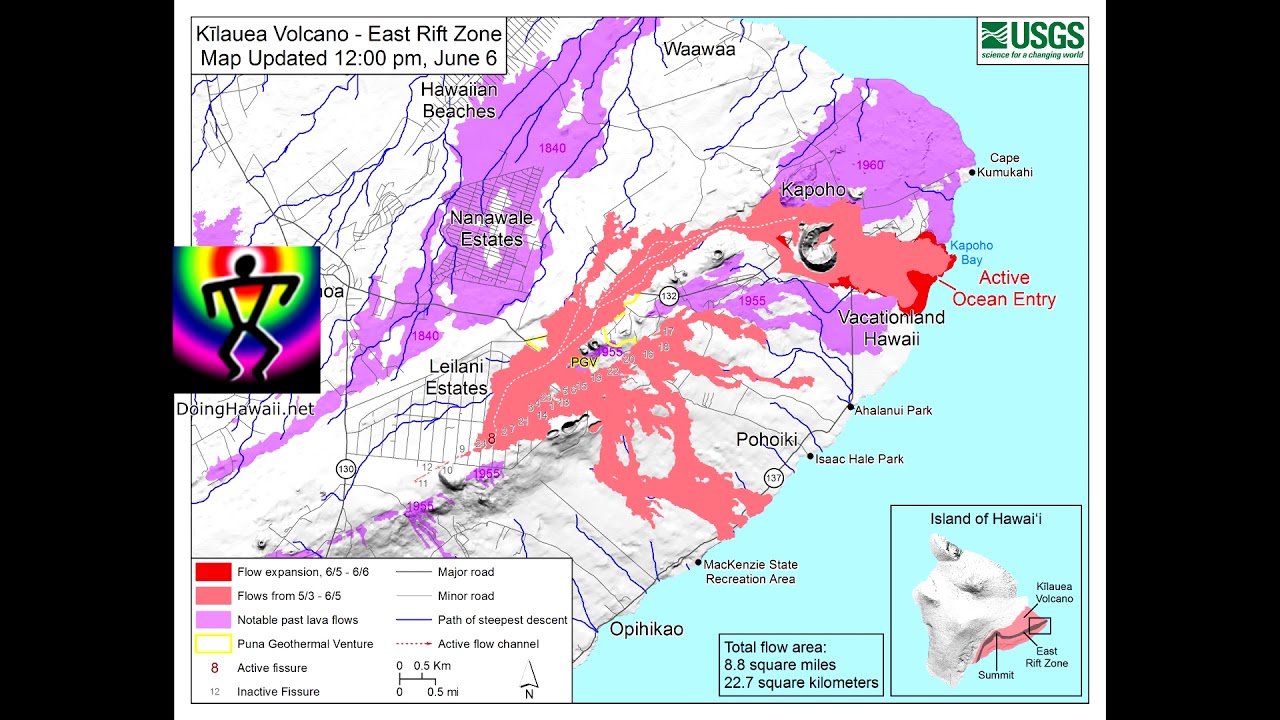
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Fiery Path: Understanding Lava Flow Maps in Hawaii. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!