Visualizing Data and Ideas: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps in PowerPoint
Related Articles: Visualizing Data and Ideas: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps in PowerPoint
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data and Ideas: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps in PowerPoint. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing Data and Ideas: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps in PowerPoint

PowerPoint, the ubiquitous presentation software, has long been a tool for conveying information and ideas visually. While commonly associated with text-heavy slides and bullet points, PowerPoint offers a powerful suite of tools for creating engaging and impactful presentations. Among these tools, maps stand out as a versatile and effective way to visualize data, illustrate concepts, and enhance audience understanding.
The Power of Visual Representation
Maps, in their various forms, have been instrumental in human understanding for millennia. They provide a spatial context for information, allowing us to see patterns, relationships, and trends that might otherwise be obscured by data alone. This inherent power of visualization translates seamlessly into the realm of presentations.
Beyond Static Images: Dynamic Maps in PowerPoint
PowerPoint’s map functionality extends beyond static images, offering dynamic and interactive elements that elevate presentations. These capabilities include:
- Customizable Maps: PowerPoint allows users to select from a wide range of map types, including world maps, regional maps, and even custom maps tailored to specific needs. This flexibility ensures that the map accurately reflects the data being presented.
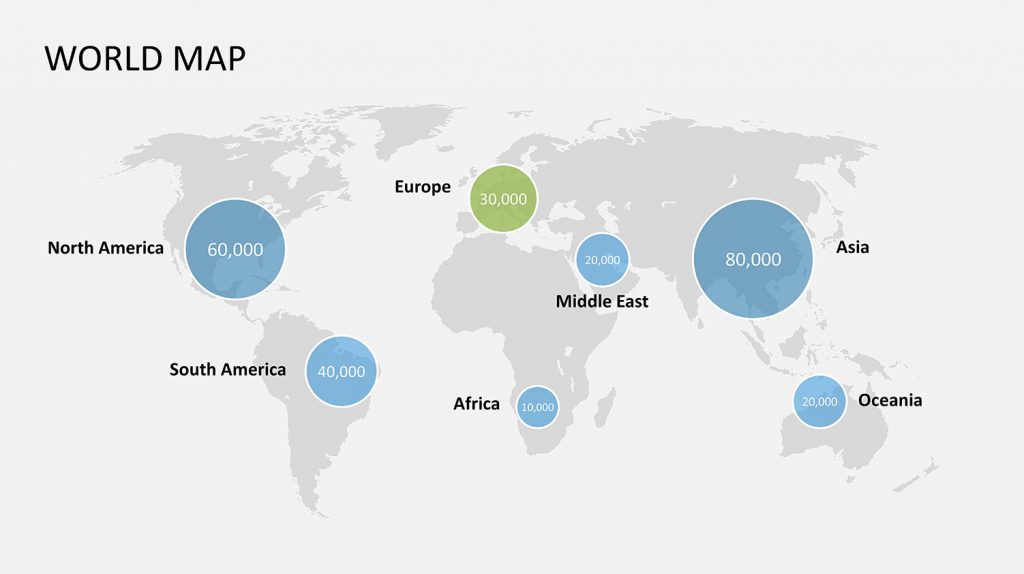
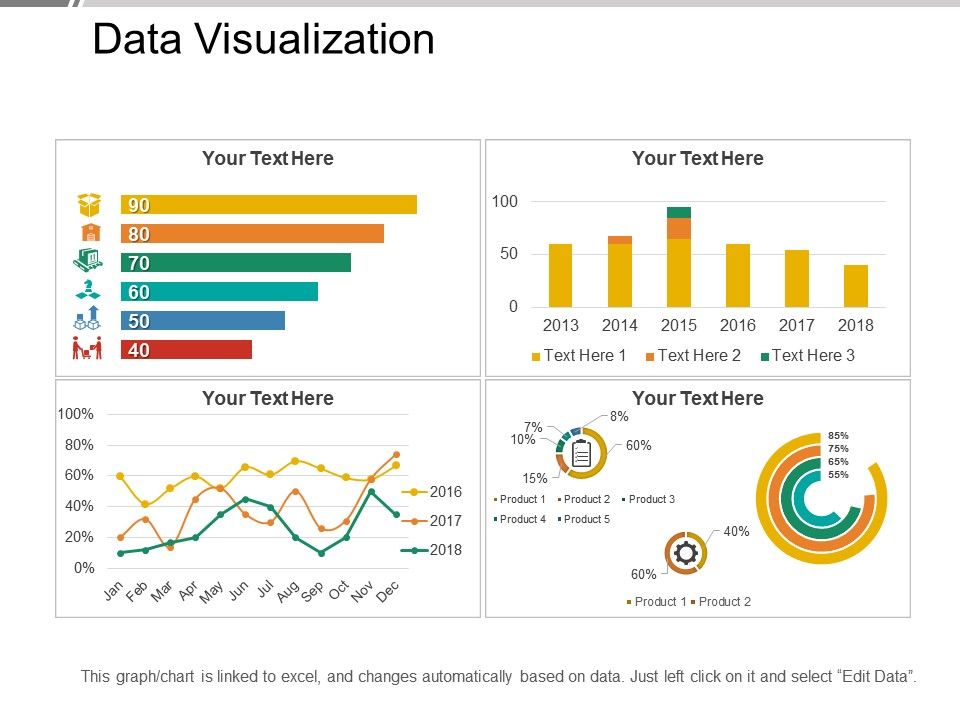
- Data Visualization: Maps can be overlaid with data points, heatmaps, and other visual elements to showcase trends, distribution, and relationships. This allows for a clear and compelling representation of complex data sets.
- Interactive Elements: PowerPoint allows for the creation of interactive maps that respond to user input. This can include zooming, panning, and highlighting specific areas, enhancing audience engagement and facilitating data exploration.
- Animations and Transitions: Maps can be animated to reveal data points sequentially, highlight specific areas, or showcase changes over time. These dynamic effects add visual interest and facilitate understanding.
Applications of Maps in PowerPoint Presentations
The versatility of maps in PowerPoint extends across various industries and presentation types, including:
- Business Presentations: Maps can illustrate sales territories, customer demographics, market share, and distribution networks, providing valuable insights for strategic planning and decision-making.
- Marketing Presentations: Maps can effectively showcase target markets, customer segmentation, and campaign reach, optimizing marketing efforts and understanding audience behavior.
- Education and Training: Maps can visualize historical events, geographical features, and scientific data, providing engaging and informative learning experiences.
- Research Presentations: Maps can be used to present research findings, illustrate geographic trends, and highlight areas of focus, enhancing the impact and clarity of research presentations.
- Project Management: Maps can visualize project timelines, resource allocation, and project dependencies, offering a clear and concise overview of project progress and potential challenges.
Beyond Data: Utilizing Maps for Conceptual Illustration
Beyond visualizing data, maps can be used to effectively illustrate concepts and ideas, particularly those with spatial or geographical relevance. This includes:
- Product Launches: Maps can be used to showcase global reach, target markets, and distribution channels, emphasizing the global impact of a product launch.
- Strategic Planning: Maps can visualize strategic goals, market expansion plans, and competitive landscapes, providing a clear visual representation of strategic direction.
- Organizational Structure: Maps can be used to visually represent organizational hierarchies, departmental relationships, and communication channels, offering a clear and concise overview of organizational structure.
- Process Mapping: Maps can be used to visualize workflows, operational processes, and customer journeys, providing a clear understanding of complex systems and potential areas for improvement.
FAQs about Maps in PowerPoint
Q: What are the key considerations when creating maps in PowerPoint?
A: When creating maps in PowerPoint, it’s essential to consider:
- Data Accuracy: Ensure that the data used to create the map is accurate and reliable.
- Map Clarity: Choose a map style and design that is clear and easy to understand. Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information.
- Visual Appeal: Utilize colors, icons, and other visual elements to make the map engaging and visually appealing.
- Interactive Elements: Consider incorporating interactive elements, such as zooming, panning, and highlighting, to enhance audience engagement and facilitate data exploration.
Q: How can I ensure that my map is visually appealing and effective?
A: To create visually appealing and effective maps in PowerPoint:
- Choose the Right Map Type: Select a map type that best suits the data being presented and the message being conveyed.
- Use Color Effectively: Choose a color scheme that is both visually appealing and conveys the data effectively.
- Simplify and Focus: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information. Focus on the key data points and insights.
- Use Icons and Symbols: Incorporate icons and symbols to represent data points and enhance visual clarity.
Q: What are some tips for creating interactive maps in PowerPoint?
A: To create interactive maps in PowerPoint:
- Utilize PowerPoint’s built-in features: Explore PowerPoint’s built-in features for creating interactive elements, such as hyperlinks, animations, and transitions.
- Use Third-Party Tools: Consider using third-party tools, such as mapping software or data visualization tools, to create more advanced interactive maps.
- Test Thoroughly: Ensure that the interactive elements are working correctly and that the map is responsive to user input.
Q: How can I integrate maps with other presentation elements?
A: To seamlessly integrate maps with other presentation elements:
- Consistent Design: Ensure that the map’s style and design align with the overall presentation theme.
- Clear Transitions: Use smooth transitions to move between slides that contain maps and other presentation elements.
- Data Consistency: Ensure that the data presented in the map is consistent with other data sources used in the presentation.
Tips for Creating Effective Maps in PowerPoint
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of the map and the message you want to convey.
- Choose the right map type: Select a map type that best suits the data being presented and the message being conveyed.
- Use data wisely: Ensure that the data used to create the map is accurate, relevant, and presented in a clear and concise manner.
- Focus on visual clarity: Use colors, icons, and other visual elements to make the map easy to understand and interpret.
- Keep it simple: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information. Focus on the key data points and insights.
- Consider interactivity: Explore the use of interactive elements to enhance audience engagement and facilitate data exploration.
Conclusion: Maps as a Powerful Tool for Visual Communication
Maps, in their various forms, offer a powerful tool for visual communication in PowerPoint presentations. By leveraging the capabilities of maps, presenters can effectively visualize data, illustrate concepts, and enhance audience understanding. From showcasing sales territories to presenting research findings, maps provide a clear and compelling way to communicate complex information and engage audiences. As technology continues to evolve, the power of maps in PowerPoint will only continue to grow, offering new and innovative ways to visualize data and ideas.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data and Ideas: A Comprehensive Guide to Maps in PowerPoint. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!