Guinea-Bissau: A Nation of Islands and Coastline on the Western Edge of Africa
Related Articles: Guinea-Bissau: A Nation of Islands and Coastline on the Western Edge of Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Guinea-Bissau: A Nation of Islands and Coastline on the Western Edge of Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Guinea-Bissau: A Nation of Islands and Coastline on the Western Edge of Africa
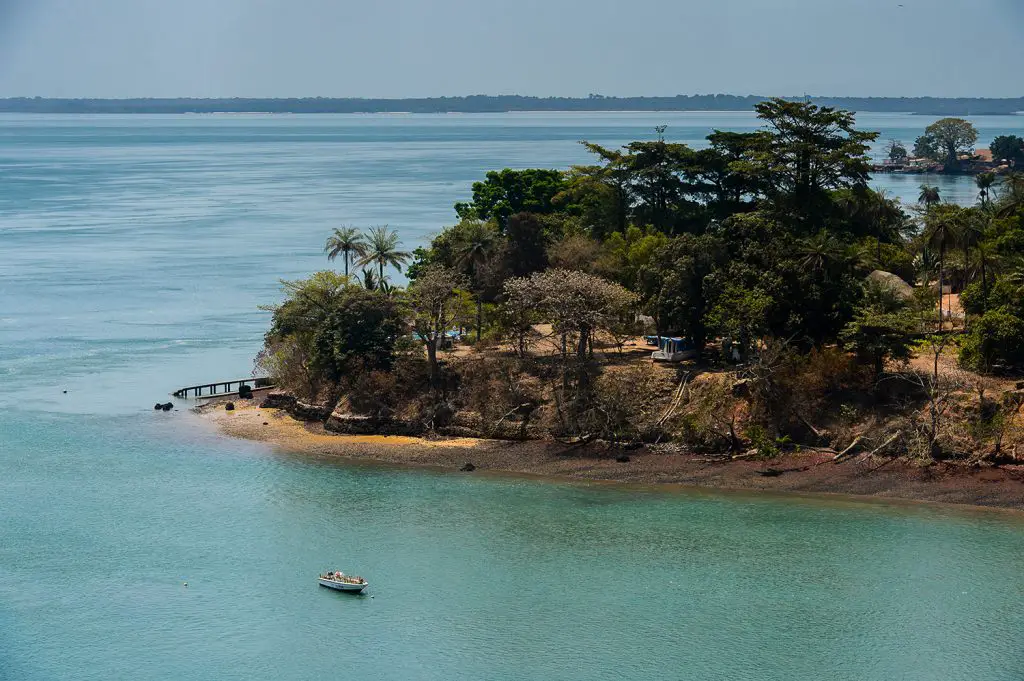

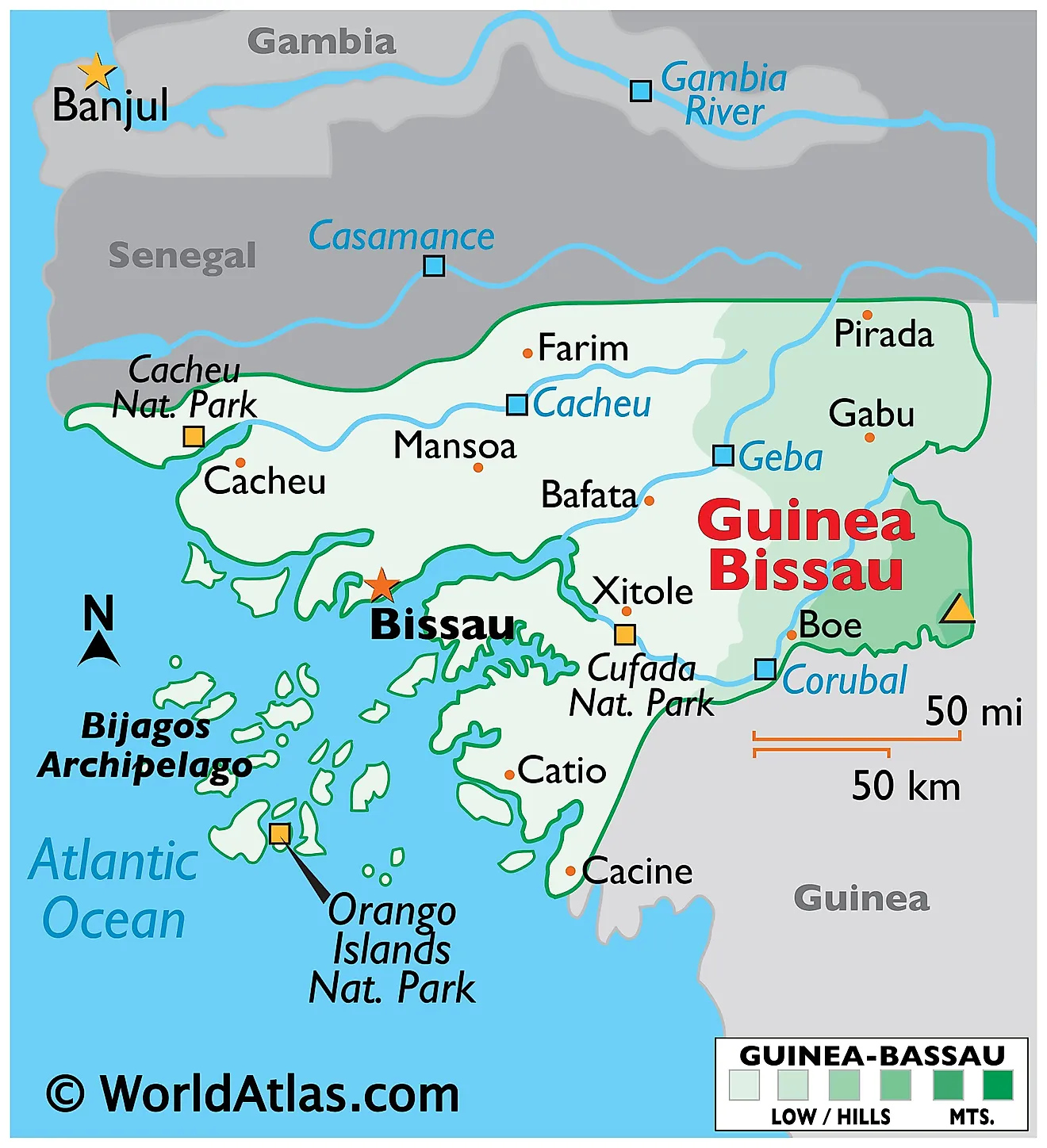
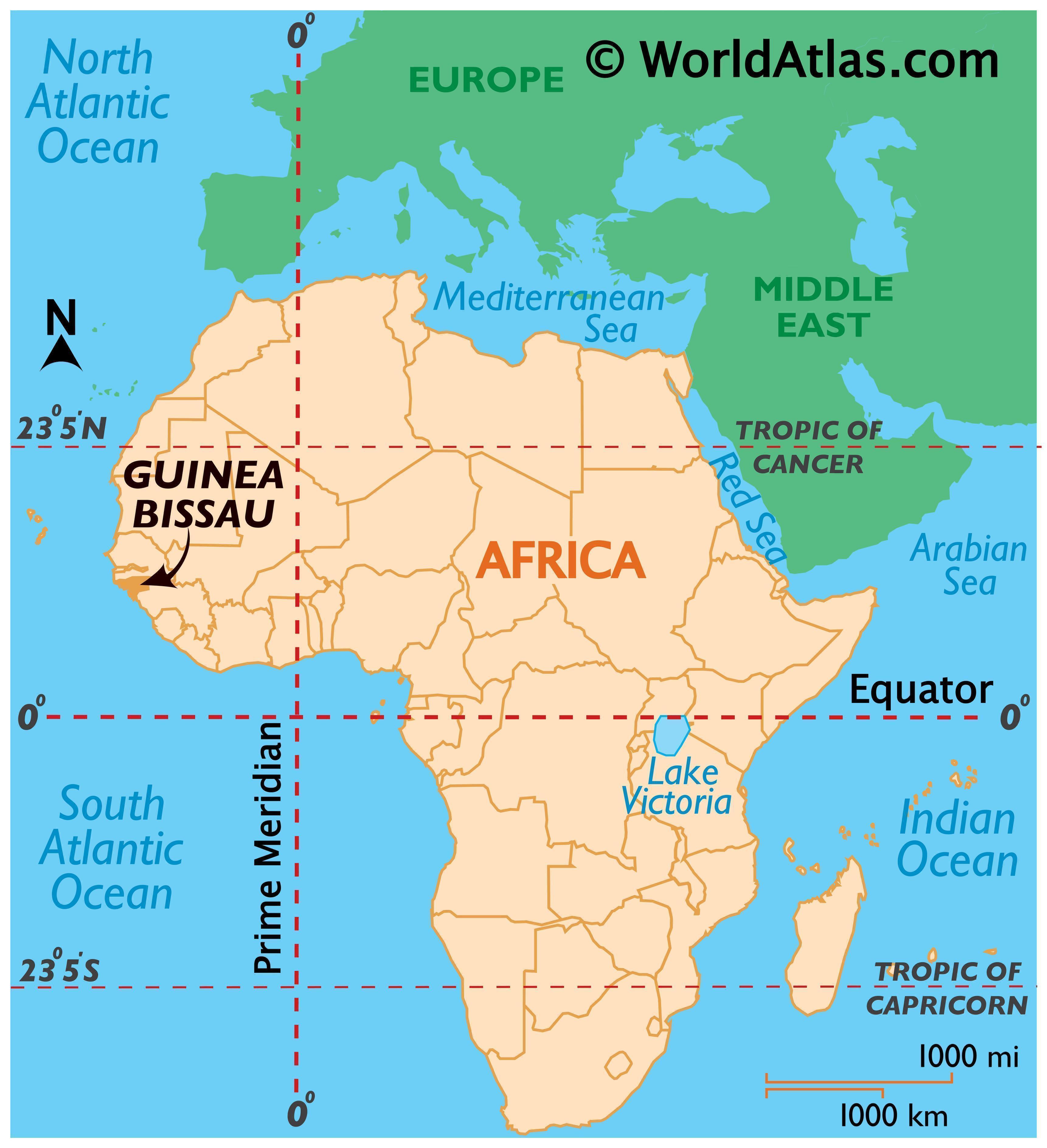
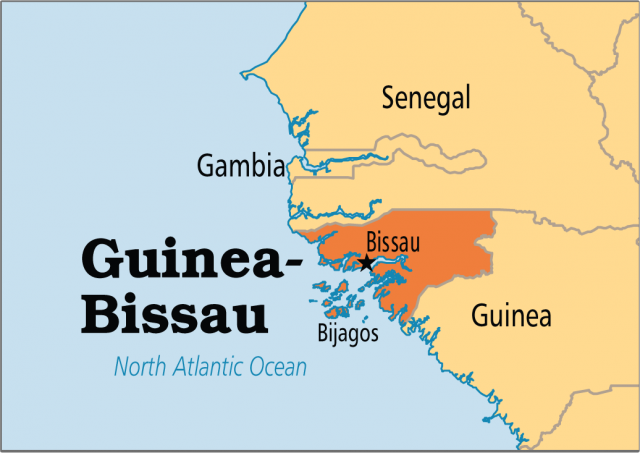
Guinea-Bissau, a small West African nation, occupies a unique geographic position, nestled between Senegal and the Atlantic Ocean. Its intricate coastline, punctuated by numerous islands and archipelagos, shapes its identity and influences its economic and cultural landscape. Understanding the nation’s location on the map provides a crucial lens through which to examine its history, challenges, and potential.
A Glimpse into the Geography
Guinea-Bissau’s territory stretches across a narrow coastal strip, bordered by Senegal to the north and east. The Bijagos Archipelago, a collection of islands and islets, lies just off the coast, adding to the nation’s maritime diversity. The country’s landscape is dominated by low-lying plains, interspersed with mangrove forests, savannas, and the meandering courses of the Geba and Corubal rivers.
The Bijagos Archipelago, comprising over 88 islands and islets, holds significant ecological importance. These islands serve as nesting grounds for numerous bird species, including the endangered African fish eagle, and provide vital habitats for diverse marine life. The archipelago’s unique ecosystem, characterized by its tidal forests and lagoons, is recognized as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve.
Historical Significance and Colonial Past
Guinea-Bissau’s strategic location along the Atlantic coast played a vital role in its historical development. The region was initially inhabited by various ethnic groups, including the Mandinka, Balanta, and Fula people. European influence arrived in the 15th century with Portuguese explorers seeking trade routes to the East. The Portuguese established trading posts and later claimed the territory as a colony, naming it Portuguese Guinea.
Guinea-Bissau’s history is marked by a long struggle for independence. The African Party for the Independence of Guinea and Cape Verde (PAIGC) led a protracted armed struggle against Portuguese rule, culminating in the country’s independence in 1973. This struggle for liberation continues to influence the nation’s political and social landscape.
Economic Landscape and Challenges
Despite its rich natural resources, including fertile land, abundant fisheries, and significant mineral deposits, Guinea-Bissau faces significant economic challenges. The nation’s economy remains heavily reliant on agriculture, primarily the production of cashew nuts, which are susceptible to price fluctuations in the global market. Other key sectors include fishing, forestry, and tourism.
The country has experienced political instability and recurrent military coups, hindering economic development. Corruption, lack of infrastructure, and limited access to education and healthcare further compound these challenges. However, Guinea-Bissau has shown resilience and is striving to diversify its economy, promote sustainable agriculture, and attract foreign investment.
Cultural Tapestry and Artistic Expressions
Guinea-Bissau’s rich cultural heritage is a blend of traditional African customs and Portuguese influences. The nation is renowned for its vibrant music, dance, and storytelling traditions. The traditional musical instrument, the balafon, a wooden xylophone, holds a prominent place in the country’s cultural landscape.
The country’s artistic expressions reflect its history and unique cultural identity. Traditional crafts, including weaving, woodcarving, and pottery, are practiced and celebrated. The annual Festival of the Arts in Bissau, the capital city, showcases the diverse artistic talents of the nation.
Navigating the Future: Opportunities and Challenges
Guinea-Bissau faces a multitude of challenges in its quest for sustainable development. However, the nation also possesses significant potential. Its strategic location, rich natural resources, and vibrant culture offer opportunities for economic growth and social progress.
The country’s focus on promoting tourism, developing its infrastructure, and fostering regional cooperation holds promise for a brighter future. Strengthening governance, promoting transparency, and investing in human capital will be crucial for achieving lasting stability and prosperity.
FAQs on Guinea-Bissau
1. What is the capital city of Guinea-Bissau?
The capital city of Guinea-Bissau is Bissau, situated on the Atlantic coast.
2. What languages are spoken in Guinea-Bissau?
The official language of Guinea-Bissau is Portuguese. However, numerous local languages are spoken throughout the country, including Crioulo, Mandinka, Balanta, and Fula.
3. What is the climate like in Guinea-Bissau?
Guinea-Bissau experiences a tropical climate with high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The rainy season typically runs from May to November, while the dry season extends from December to April.
4. What are the main industries in Guinea-Bissau?
The primary industries in Guinea-Bissau are agriculture, fishing, forestry, and tourism. Cashew nut production remains a significant contributor to the national economy.
5. What are some of the key tourist attractions in Guinea-Bissau?
Guinea-Bissau offers a unique blend of natural beauty and cultural attractions. The Bijagos Archipelago, with its pristine beaches, mangrove forests, and diverse wildlife, is a popular destination for eco-tourism. The capital city, Bissau, features historical landmarks, vibrant markets, and a rich cultural scene.
Tips for Visiting Guinea-Bissau
- Visa Requirements: Ensure you have the necessary travel documents and visas before traveling to Guinea-Bissau.
- Currency: The official currency of Guinea-Bissau is the West African CFA franc (XOF).
- Health Precautions: Consult with your doctor regarding recommended vaccinations and health precautions before traveling.
- Language: While Portuguese is the official language, learning basic phrases in Crioulo, the national language, can be helpful.
- Respectful Travel: Be mindful of local customs and traditions, dress modestly, and avoid public displays of affection.
Conclusion
Guinea-Bissau, a nation of islands and coastline, stands as a testament to the resilience and diversity of West Africa. Despite its challenges, the nation possesses a rich history, a vibrant culture, and a promising future. Understanding its geography, history, and cultural landscape provides a valuable perspective on its unique identity and its ongoing journey towards sustainable development. As the nation continues to navigate its path forward, its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and unwavering spirit offer a compelling vision for a brighter future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Guinea-Bissau: A Nation of Islands and Coastline on the Western Edge of Africa. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!