Navigating California’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating California’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating California’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating California’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide
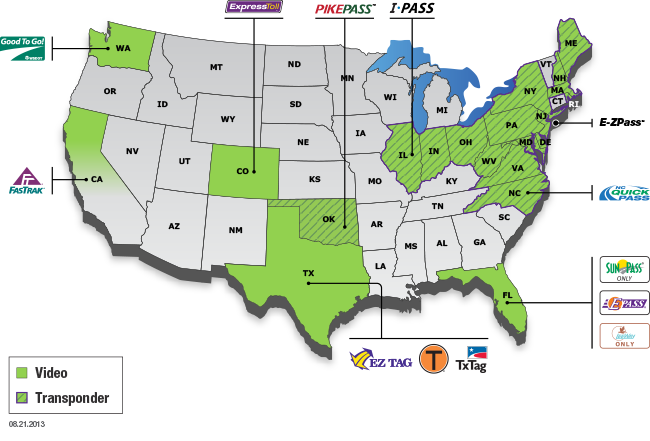
California’s vast network of toll roads offers drivers a faster, more efficient way to traverse the state, but navigating this system can be daunting. This article provides a comprehensive overview of California’s toll roads, examining their geographical distribution, payment methods, and potential benefits for drivers.
Understanding the Network
California’s toll roads are operated by various entities, including the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans), the California Transportation Commission (CTC), and private toll road operators. These roads are primarily concentrated in urban and suburban areas, offering alternatives to congested freeways.
Key Toll Road Systems
- The 91 Express Lanes (Orange County): This 10-mile stretch of the 91 Freeway features express lanes that provide a faster commute option for Orange County residents.
- The 134 Express Lanes (Los Angeles County): Extending from the 101 Freeway to the 210 Freeway, these lanes offer a time-saving alternative for drivers navigating the San Fernando Valley.
- The 101 Express Lanes (Los Angeles County): These lanes, primarily located in the Sepulveda Pass, provide a quicker route for drivers traveling between the San Fernando Valley and West Los Angeles.
- The 57 Freeway Express Lanes (Orange County): These lanes, located on the 57 Freeway between the 91 Freeway and the 60 Freeway, provide a faster travel option for drivers in the Orange County area.
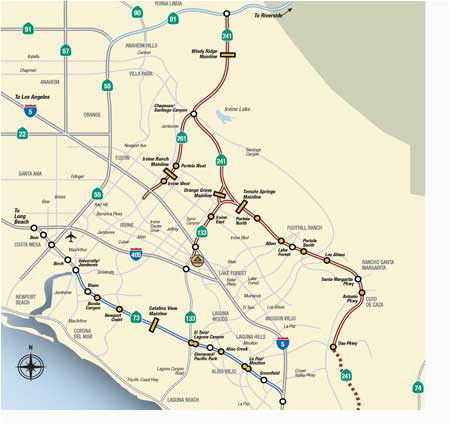
- The 241 Toll Road (Orange County): This 16-mile toll road connects the 91 Freeway to the 5 Freeway, providing a more direct route for drivers traveling between Orange County and the Inland Empire.
- The 73 Toll Road (Orange County): This 14-mile toll road connects the 5 Freeway to the 405 Freeway, offering a faster alternative for drivers traveling through Orange County.
- The 101 Toll Road (Ventura County): This 12-mile toll road connects the 101 Freeway to the 118 Freeway, providing a faster route for drivers traveling between Ventura County and the San Fernando Valley.
- The 126 Toll Road (Ventura County): This 13-mile toll road connects the 101 Freeway to the 230 Freeway, offering a faster route for drivers traveling between Ventura County and the Santa Clarita Valley.
- The 134 Toll Road (Los Angeles County): This 13-mile toll road connects the 101 Freeway to the 210 Freeway, providing a faster route for drivers traveling between the San Fernando Valley and the Westside of Los Angeles.
- The 152 Toll Road (Monterey County): This 14-mile toll road connects the 101 Freeway to the 152 Freeway, providing a faster route for drivers traveling between the Salinas Valley and the San Joaquin Valley.
- The 237 Toll Road (Santa Clara County): This 10-mile toll road connects the 101 Freeway to the 680 Freeway, providing a faster route for drivers traveling between the San Francisco Bay Area and the Silicon Valley.
- The 580 Toll Road (Alameda County): This 8-mile toll road connects the 580 Freeway to the 880 Freeway, providing a faster route for drivers traveling between the East Bay and the South Bay.
Payment Methods
California’s toll roads offer various payment options for drivers:
- FasTrak: This electronic toll collection system allows drivers to pay tolls automatically using a transponder attached to their vehicle. FasTrak accounts can be managed online or through a mobile app, and drivers can opt for automatic toll payment or pay tolls manually.
- License Plate Recognition (LPR): This technology captures the license plate number of vehicles that do not have a FasTrak transponder. Toll bills are then mailed to the registered owner of the vehicle.
- Cash Payment: Some toll roads accept cash payments at toll booths. However, this option may lead to longer wait times, especially during peak hours.
Benefits of Toll Roads
- Reduced Congestion: Toll roads offer a faster and more efficient way to travel, especially during peak hours. This can significantly reduce travel time and improve traffic flow on adjacent freeways.
- Improved Safety: The dedicated lanes and reduced congestion on toll roads can improve safety by minimizing instances of lane changes and sudden braking.
- Increased Revenue: Toll revenue is used to fund road maintenance, construction, and other transportation projects, contributing to the overall improvement of California’s transportation infrastructure.
- Environmental Benefits: By reducing congestion, toll roads can reduce vehicle emissions and improve air quality.
Challenges and Criticisms
While toll roads offer numerous benefits, they also face criticism and challenges:
- Cost: Toll roads can be expensive, especially for frequent users.
- Equity: Critics argue that toll roads disproportionately impact low-income communities, who may not have the financial resources to afford the tolls.
- Transparency: Some argue that the process for setting toll rates lacks transparency and accountability.
- Environmental Impact: The construction and operation of toll roads can have environmental impacts, such as habitat fragmentation and increased noise pollution.
FAQs
Q: Are toll roads mandatory in California?
A: No, toll roads are not mandatory. Drivers have the option to use freeways or other alternative routes. However, toll roads offer a faster and more efficient travel option, especially during peak hours.
Q: How can I avoid paying tolls on California toll roads?
A: There are no guaranteed ways to avoid paying tolls on California toll roads. However, drivers can utilize alternative routes, travel during off-peak hours, or use public transportation to minimize their exposure to toll costs.
Q: What happens if I don’t pay a toll?
A: If you do not pay a toll within a specific timeframe, you will receive a toll violation notice in the mail. Failure to pay the violation may result in fines and penalties, and even the suspension of your driver’s license.
Q: How can I get a FasTrak transponder?
A: You can purchase a FasTrak transponder online, at participating retailers, or at Caltrans toll plazas.
Tips for Using Toll Roads
- Plan your route in advance: Use a navigation app or website to plan your route and determine if toll roads are a viable option.
- Consider the time of day: Toll roads can be congested during peak hours. Consider traveling during off-peak hours to avoid traffic and tolls.
- Sign up for a FasTrak account: Having a FasTrak transponder will allow you to pay tolls automatically and avoid delays at toll booths.
- Monitor your account: Regularly check your FasTrak account for any toll violations or outstanding charges.
- Stay informed about toll rates: Toll rates can vary depending on the time of day, day of the week, and location. Keep up-to-date on the latest toll rates to budget accordingly.
Conclusion
California’s toll road network offers a valuable alternative for drivers seeking a faster and more efficient way to travel. While toll roads present challenges and criticisms, they also contribute to the overall improvement of the state’s transportation infrastructure and offer numerous benefits, including reduced congestion, enhanced safety, and increased revenue for transportation projects. By understanding the network, payment methods, and potential benefits, drivers can make informed decisions about using toll roads and navigate California’s roads effectively.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating California’s Toll Roads: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!