Decoding Your Backyard’s Potential: A Deep Dive into the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Associated Articles: Decoding Your Backyard’s Potential: A Deep Dive into the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing subject associated to Decoding Your Backyard’s Potential: A Deep Dive into the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Let’s weave fascinating data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding Your Backyard’s Potential: A Deep Dive into the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
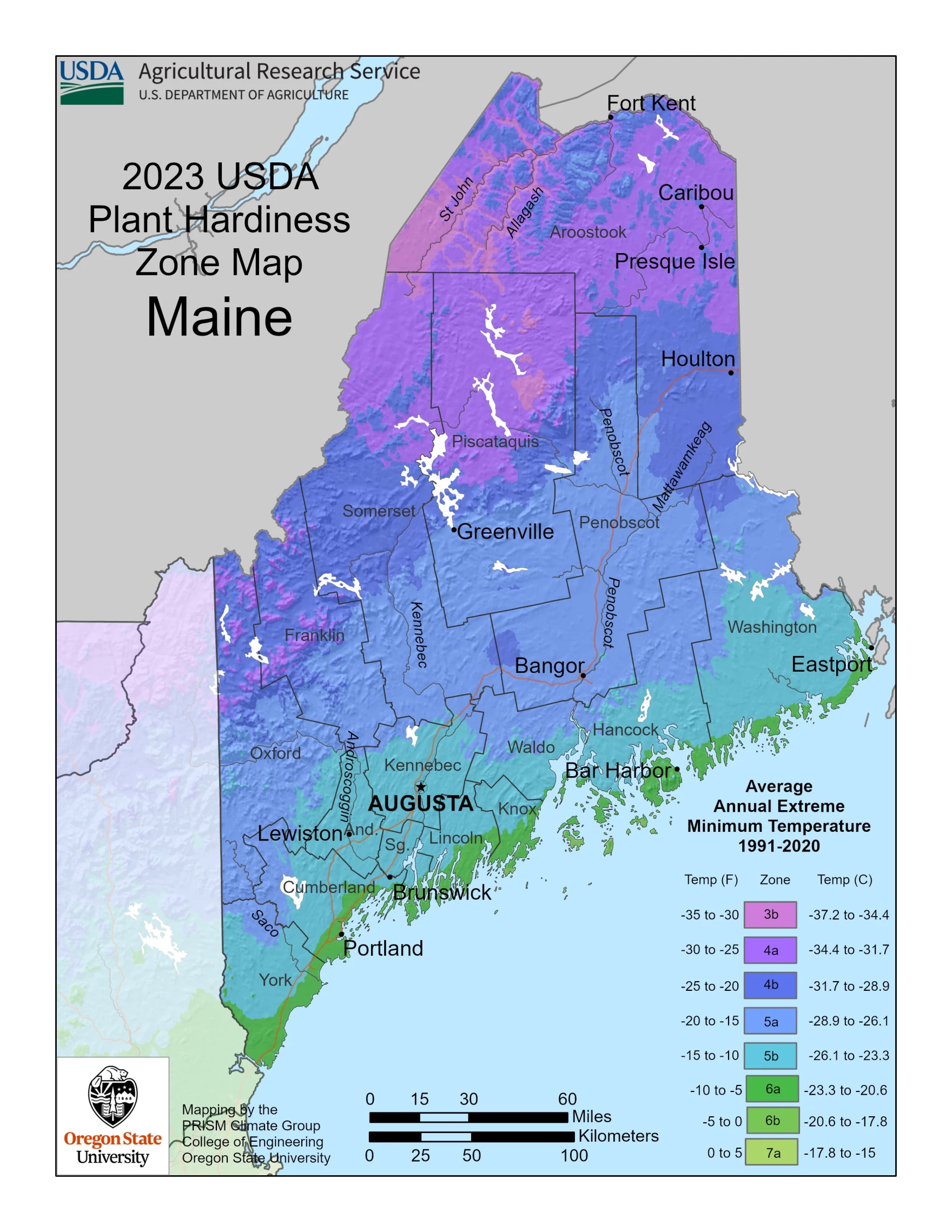
The colourful tapestry of a thriving backyard is a testomony to cautious planning and understanding of the setting. One essential component usually ignored by aspiring gardeners is the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. This seemingly easy map is a strong software, offering an important framework for choosing crops that may flourish – and even survive – in a particular location. Understanding its intricacies can remodel gardening from a chance right into a assured and rewarding endeavor.
America Division of Agriculture (USDA) Plant Hardiness Zone Map categorizes areas in North America based mostly on their common annual minimal winter temperatures. This seemingly simple metric is the muse upon which gardeners construct their planting plans, providing a dependable prediction of a plant’s capacity to resist the coldest temperatures of a selected area. Whereas different elements like soil kind, daylight publicity, and rainfall contribute to a plant’s success, the hardiness zone offers an important start line, eliminating the danger of planting unsuitable species.
The Zone System: Extra Than Simply Numbers
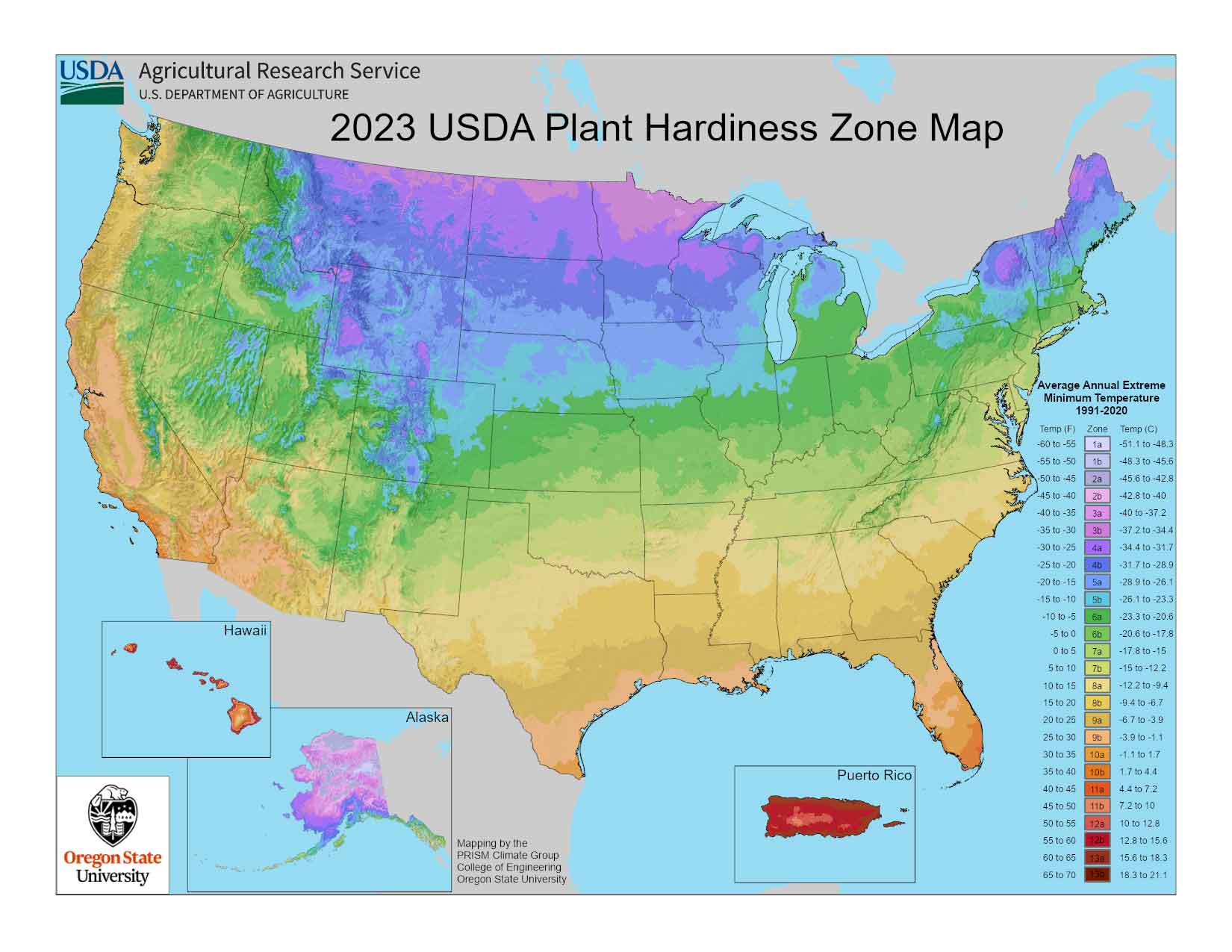
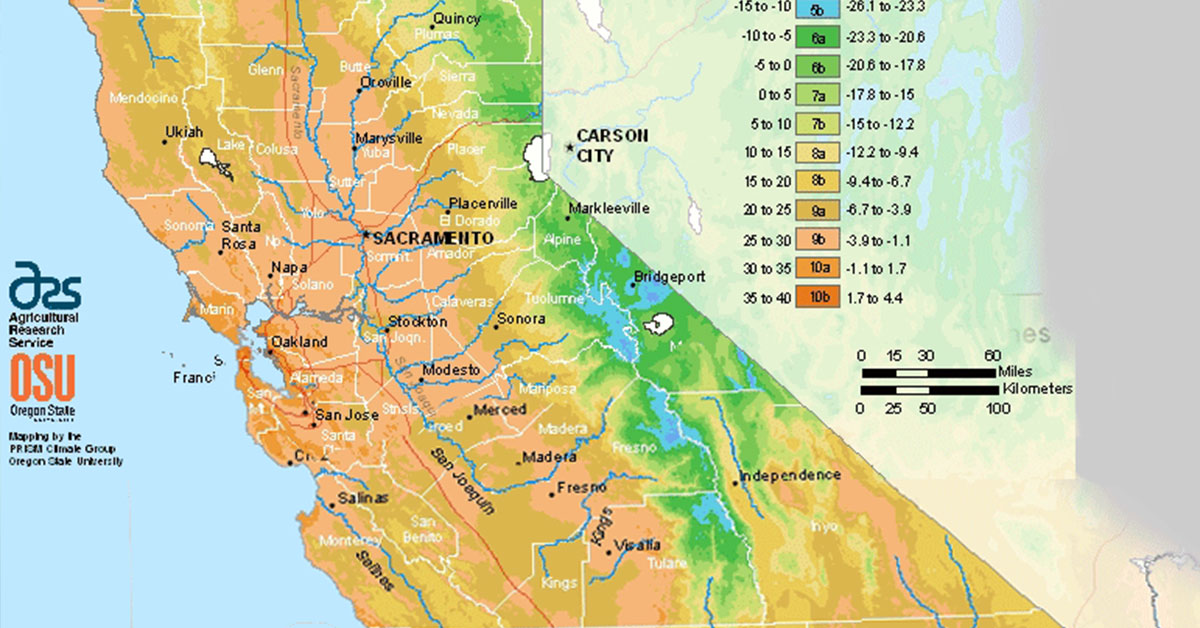
The map is split into 13 zones, every representing a ten° Fahrenheit vary of common annual minimal winter temperatures. Zone 1 represents the coldest areas, with common annual minimal temperatures under -50°F (-45°C), whereas Zone 13 represents the warmest, with common annual minimal temperatures above 65°F (18°C). Inside every zone, there are additional subdivisions, denoted by ‘a’ and ‘b’, representing a 5° Fahrenheit distinction. For instance, Zone 7a signifies a mean annual minimal temperature between 0°F and 5°F (-18°C and -15°C), whereas Zone 7b signifies a mean annual minimal temperature between 5°F and 10°F (-15°C and -12°C).
This seemingly small distinction might be important. A plant labeled as hardy to Zone 7a may battle and even perish in a Zone 7b local weather, highlighting the significance of paying shut consideration to those subdivisions. The ‘a’ and ‘b’ designations replicate the microclimates inside a broader zone, accounting for variations in elevation, proximity to water our bodies, and concrete warmth island results.
Past the Temperature: Components Influencing Plant Hardiness
Whereas the common annual minimal temperature is the first determinant of a plant’s hardiness zone, it is essential to acknowledge that different elements can considerably affect a plant’s success:
-
Microclimates: Even inside a single hardiness zone, microclimates exist. A south-facing slope will obtain extra daylight and be hotter than a north-facing slope. Proximity to giant our bodies of water can average temperatures, creating milder microclimates. City areas usually expertise increased temperatures because of the "city warmth island impact," creating hotter microclimates than surrounding rural areas.
-
Soil Kind and Drainage: Properly-drained soil is essential for stopping root rot, a typical reason behind plant demise. Completely different crops have various soil preferences, and understanding your soil kind is important for choosing appropriate crops.
-
Daylight Publicity: The quantity of daylight a plant receives straight impacts its progress and survival. Crops labeled as "sun-loving" will battle in shady areas, whereas shade-tolerant crops might not thrive in full solar.
-
Rainfall and Humidity: Water availability is a essential issue. Some crops thrive in dry situations, whereas others require persistently moist soil. Humidity ranges additionally affect plant well being, with some species preferring increased humidity than others.
-
Wind Publicity: Robust winds can desiccate crops, notably throughout winter. Sheltered places are perfect for crops delicate to wind injury.
Utilizing the Map Successfully: A Sensible Information
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a worthwhile software, but it surely’s not a magic bullet. To make use of it successfully, comply with these steps:
-
Find Your Zone: Discover your location on the map to find out your hardiness zone and subdivision. The USDA web site offers an interactive map for exact location identification.
-
Verify Plant Labels: Plant labels usually embrace the hardiness zone vary for that particular plant. Select crops whose hardiness zone vary encompasses your personal. Keep in mind to think about the ‘a’ and ‘b’ subdivisions.
-
Take into account Microclimates: Assess your backyard’s microclimates. Sunnier, sheltered areas may mean you can develop crops barely exterior your designated zone.
-
Analysis Particular Plant Wants: Do not solely depend on the hardiness zone. Analysis the precise wants of every plant, together with soil kind, daylight publicity, and water necessities.
-
Begin Small and Observe: Even with cautious planning, some crops won’t thrive. Begin with a couple of crops and observe their progress and response to your native situations. Regulate your gardening method based mostly in your observations.
-
Embrace Native Data: Interact with native gardeners and nurseries. They possess invaluable data about crops that thrive in your particular area and may provide customized recommendation.
The Evolving Map: Addressing Local weather Change
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map just isn’t static. Local weather change is inflicting important shifts in common temperatures, resulting in adjustments in plant hardiness zones throughout North America. The USDA periodically updates the map to replicate these adjustments, making it essential to seek the advice of the latest model. The continued warming pattern necessitates a extra dynamic method to gardening, requiring gardeners to be adaptable and knowledgeable concerning the evolving local weather situations of their area.
Conclusion: A Basis for Gardening Success
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a elementary software for profitable gardening. By understanding its intricacies and contemplating the extra elements that affect plant progress, gardeners can considerably improve their probabilities of cultivating a thriving and delightful backyard. Whereas the map offers a worthwhile framework, it is important to keep in mind that it is just one piece of the puzzle. Cautious commentary, analysis, and a willingness to adapt are essential for navigating the complexities of gardening and making a flourishing oasis in your personal yard. The map is a information, however your expertise and native data will finally form your backyard’s success.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Decoding Your Backyard’s Potential: A Deep Dive into the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!