A Journey Through the Heart of Venezuela: Exploring Lake Maracaibo and its Significance
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Heart of Venezuela: Exploring Lake Maracaibo and its Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Heart of Venezuela: Exploring Lake Maracaibo and its Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Heart of Venezuela: Exploring Lake Maracaibo and its Significance

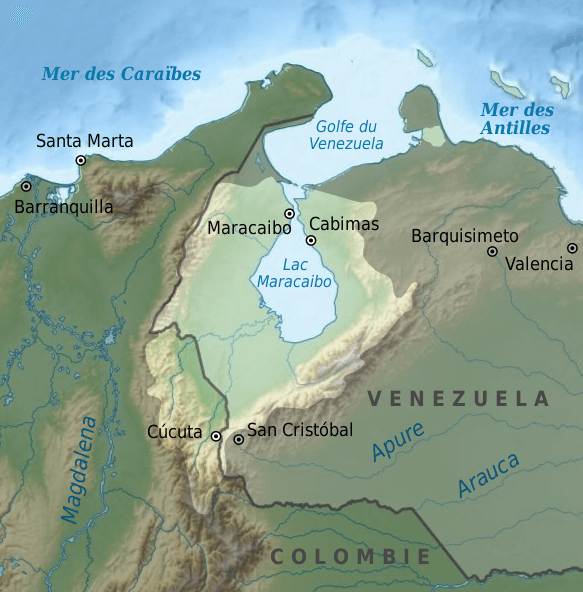
Lake Maracaibo, a vast body of water nestled in northwestern Venezuela, holds a unique place in the country’s geography, history, and economy. Its distinctive features, ranging from its unique formation to its rich biodiversity and strategic location, have shaped the region and continue to influence its present and future. This article delves into the multifaceted aspects of Lake Maracaibo, exploring its geographical characteristics, historical significance, ecological importance, and economic contributions.
A Unique Geological Formation:
Lake Maracaibo is a shallow, brackish lagoon, connected to the Caribbean Sea by a narrow channel known as the Strait of Maracaibo. This unique formation, a remnant of a much larger sea that once existed during the Miocene Epoch, makes it the largest lake in South America and the eleventh largest in the world. The lake’s distinctive shape, with its southern end tapering into a narrow neck, is a result of tectonic activity and the gradual accumulation of sediments over millions of years.
Navigating the Waters:
Lake Maracaibo’s strategic location has played a crucial role in its history. It serves as a natural gateway to the interior of Venezuela, connecting the Caribbean Sea to the Orinoco River basin. The lake’s navigable waters have facilitated trade and transportation for centuries, allowing for the movement of goods and people throughout the region. This accessibility has also made it a focal point for economic development, particularly in the oil and gas industry.
A Cradle of Oil and Gas:
The discovery of vast oil reserves beneath the lake’s floor in the early 20th century transformed Maracaibo into a hub of energy production. The "Lagoven" oil field, discovered in 1914, became the world’s largest oil field for a significant period. The lake’s rich oil and gas deposits continue to contribute significantly to Venezuela’s economy, making it a critical component of the country’s energy sector.
A Symphony of Biodiversity:
Beyond its economic significance, Lake Maracaibo is a vital ecological system, harboring a diverse array of flora and fauna. The lake’s brackish waters support a rich ecosystem, including a wide variety of fish species, reptiles, birds, and mammals. The surrounding wetlands provide critical habitat for migratory birds and serve as breeding grounds for numerous fish species. The lake’s unique environment also supports a diverse range of plant life, including mangrove forests and aquatic vegetation.
Navigating the Challenges:
Despite its economic and ecological importance, Lake Maracaibo faces a number of challenges. Pollution from oil and gas extraction, agricultural runoff, and industrial waste poses a significant threat to the lake’s ecosystem. Overfishing and habitat destruction are also contributing to the decline of fish populations and the overall health of the lake. Climate change, with its potential to increase sea levels and alter precipitation patterns, further complicates the lake’s future.
Understanding the Importance:
The challenges facing Lake Maracaibo highlight the need for sustainable management practices. Balancing the economic benefits derived from the lake with the need to protect its delicate ecosystem is a complex task. Sustainable development strategies are crucial to ensure that future generations can enjoy the benefits of this unique and valuable natural resource.
FAQs about Lake Maracaibo:
1. What is the origin of the name "Maracaibo"?
The name "Maracaibo" is believed to have originated from the indigenous word "Mara", meaning "fish", and "Cayo", meaning "island". The name likely refers to the abundance of fish in the lake and the presence of numerous islands within its waters.
2. What is the average depth of Lake Maracaibo?
The average depth of Lake Maracaibo is approximately 5 meters (16 feet), with some areas reaching depths of up to 50 meters (164 feet). The shallow depth of the lake contributes to its unique ecosystem and makes it susceptible to changes in water levels.
3. What are the major industries located around Lake Maracaibo?
The major industries located around Lake Maracaibo are primarily centered around oil and gas extraction, refining, and processing. Other industries include fishing, agriculture, and tourism. The lake’s strategic location and natural resources have made it a hub for economic activity in Venezuela.
4. What are the major environmental threats facing Lake Maracaibo?
The major environmental threats facing Lake Maracaibo include pollution from oil and gas extraction, agricultural runoff, industrial waste, overfishing, habitat destruction, and the potential impacts of climate change. These threats are jeopardizing the lake’s ecosystem and the livelihoods of the communities that depend on it.
5. What measures are being taken to protect Lake Maracaibo?
Several measures are being taken to protect Lake Maracaibo, including the implementation of environmental regulations, the establishment of protected areas, the promotion of sustainable fishing practices, and the development of environmental education programs. However, more needs to be done to address the complex challenges facing the lake.
Tips for Exploring Lake Maracaibo:
1. Visit the City of Maracaibo:
The city of Maracaibo, located on the shores of the lake, offers a glimpse into the region’s history and culture. Visit the historic center, explore the vibrant markets, and enjoy the city’s unique atmosphere.
2. Take a Boat Trip:
Experience the beauty of Lake Maracaibo by taking a boat trip across its waters. Observe the diverse wildlife, explore the surrounding islands, and enjoy the breathtaking views.
3. Visit the Zulia State Museum:
Learn about the history and culture of the Zulia region, which encompasses Lake Maracaibo, at the Zulia State Museum. Discover the region’s indigenous heritage, its colonial past, and its contemporary culture.
4. Enjoy the Local Cuisine:
Indulge in the flavors of Zulia cuisine, renowned for its rich and diverse dishes. Sample local specialties such as "Arepas" (corn cakes), "Cachapas" (corn pancakes), and "Patacones" (fried plantains).
5. Respect the Environment:
When visiting Lake Maracaibo, be mindful of the environment. Dispose of waste responsibly, avoid disturbing wildlife, and support sustainable tourism practices.
Conclusion:
Lake Maracaibo, with its unique geological formation, strategic location, and rich biodiversity, stands as a testament to the power and beauty of nature. It plays a vital role in Venezuela’s economy, providing energy resources and supporting livelihoods. However, the lake faces a number of challenges, requiring sustainable management practices to ensure its long-term health and the well-being of the communities that depend on it. By understanding the importance of Lake Maracaibo and actively working to protect its ecosystem, we can ensure that this vital resource continues to thrive for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Heart of Venezuela: Exploring Lake Maracaibo and its Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!