Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regional Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regional Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regional Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regional Map
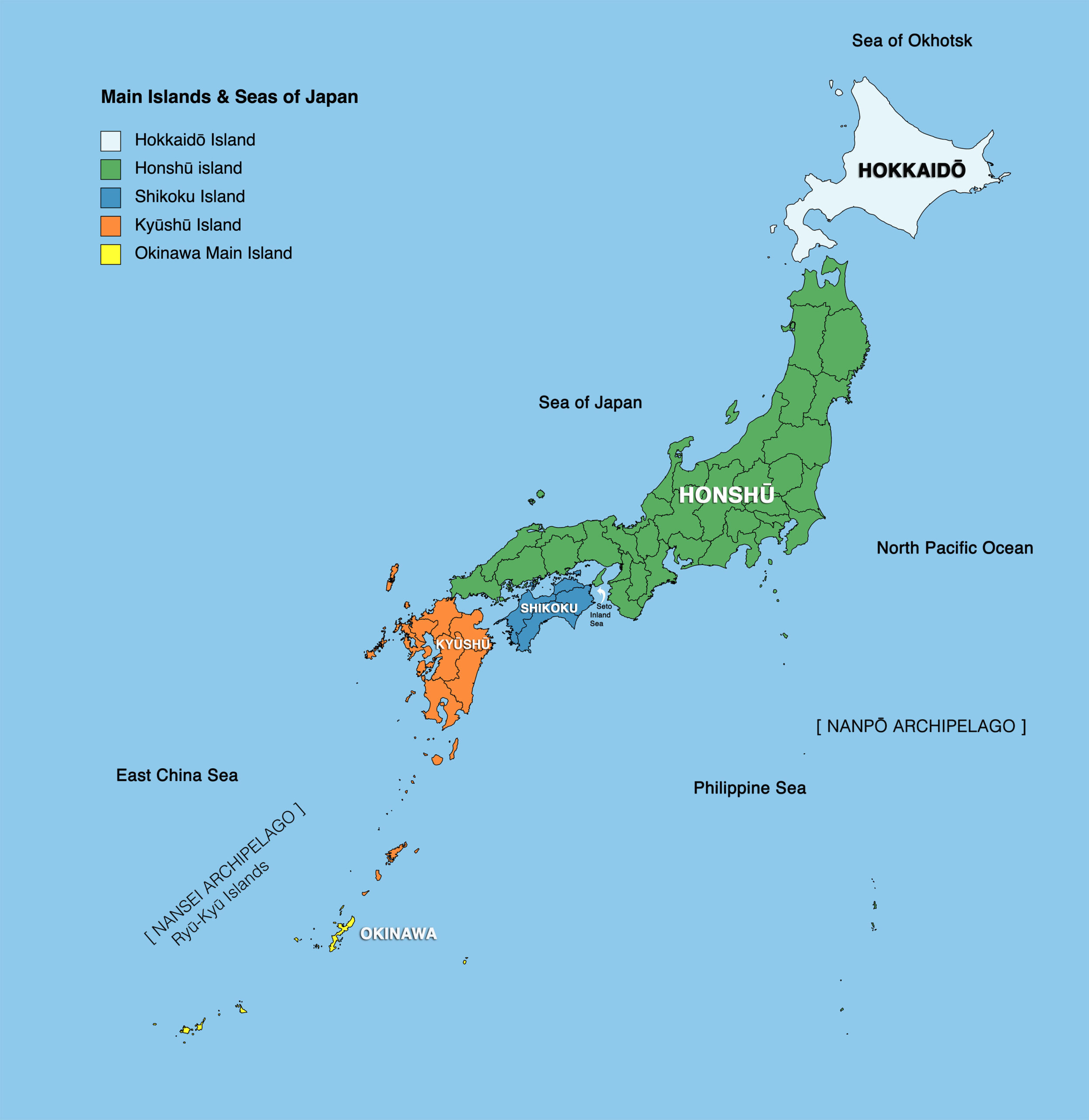
Japan, a nation of volcanic peaks, serene mountains, and bustling cities, is a tapestry of diverse landscapes and rich cultural traditions. Understanding its regional map is crucial for appreciating the country’s intricate beauty and the unique character of its people. This article delves into the geographical and cultural nuances of Japan’s regions, highlighting their distinct attributes and the significance of their interconnectedness.
Understanding Japan’s Regional Divisions
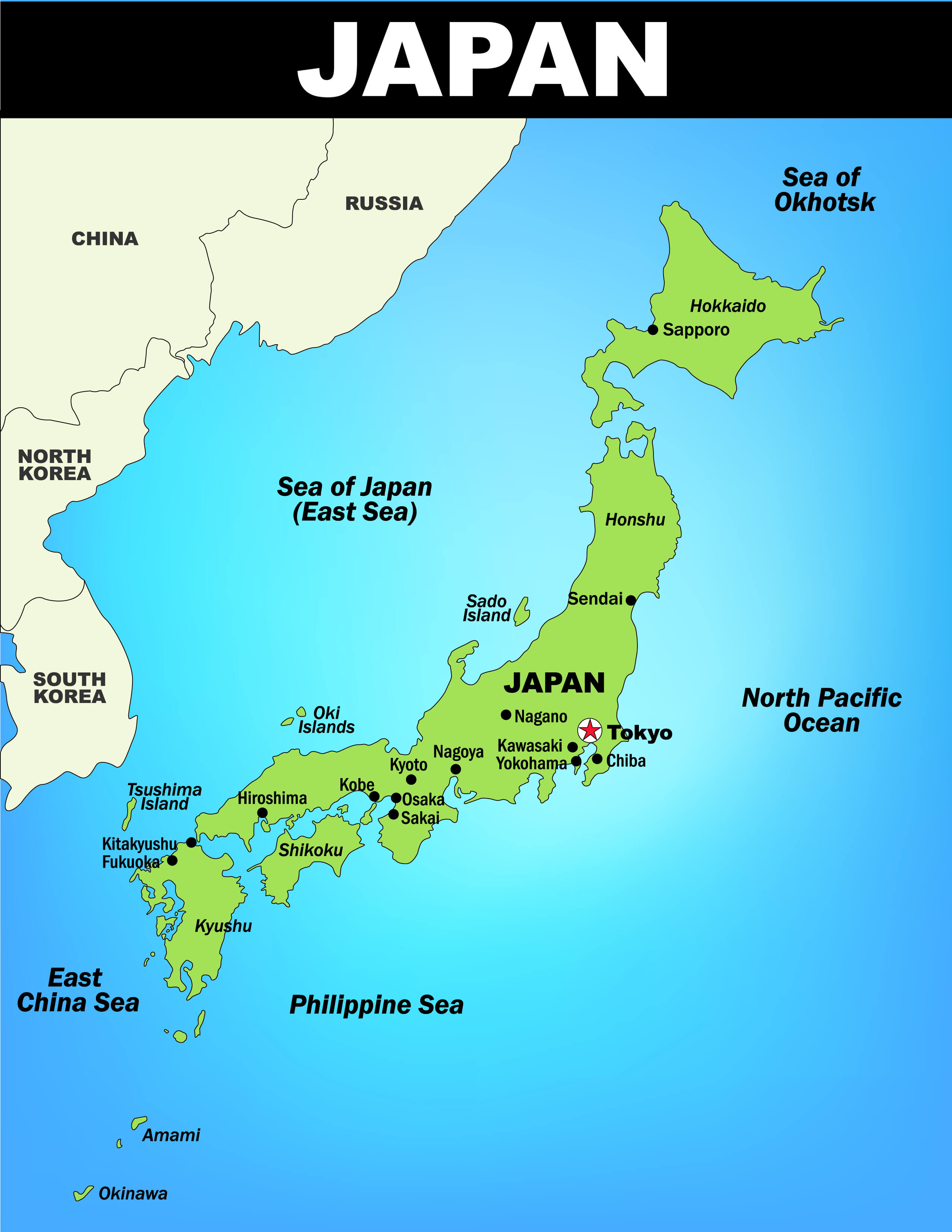
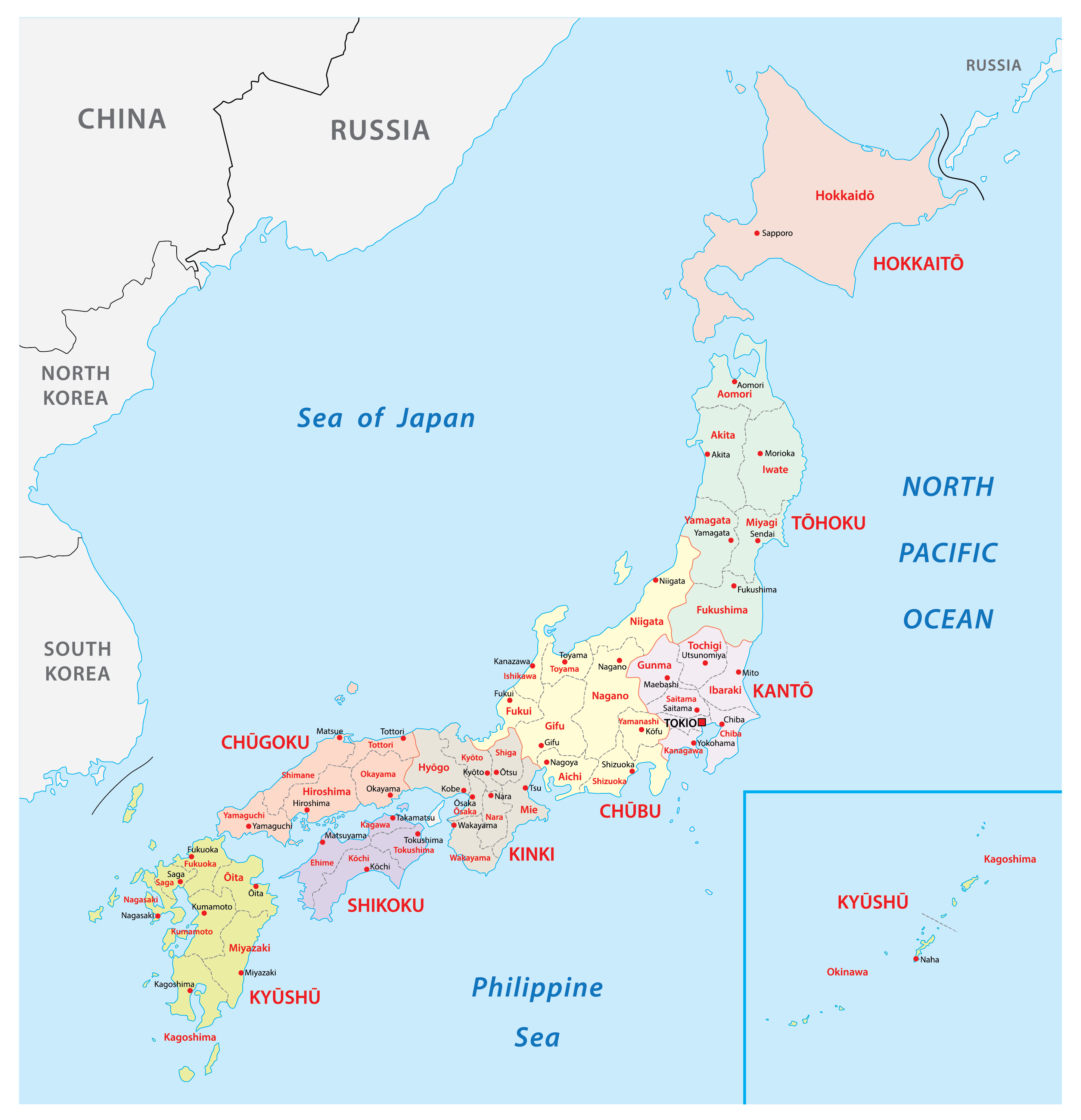
Japan’s regional map is often categorized into eight distinct areas: Hokkaido, Tohoku, Kanto, Chubu, Kansai, Chugoku, Shikoku, and Kyushu. These divisions are based on historical, geographical, and cultural factors, offering a framework for comprehending the country’s diverse tapestry.
Hokkaido: The Northern Frontier
Hokkaido, the northernmost island, is a land of rugged mountains, pristine forests, and volcanic landscapes. Known for its abundant natural resources, Hokkaido is home to vast dairy farms, fishing communities, and a thriving agricultural sector. Its distinct Ainu culture, with its unique language and traditions, adds another layer of complexity to its identity.
Tohoku: The Land of Mountains and Coasts
Tohoku, located in the northeastern region of Honshu, is characterized by its mountainous terrain and rugged coastline. Its natural beauty encompasses scenic hot springs, pristine beaches, and the iconic Matsushima Bay. The region is renowned for its traditional crafts, such as lacquerware, and its rich history, evident in the numerous samurai castles and ancient temples.
Kanto: The Heart of Japan
Kanto, encompassing Tokyo and its surrounding areas, is the economic and cultural hub of Japan. Home to bustling cities, towering skyscrapers, and world-renowned institutions, Kanto is a vibrant melting pot of innovation and tradition. Its diverse landscape, including the iconic Mount Fuji, offers a stark contrast to the urban sprawl.
Chubu: The Central Region
Chubu, located in the center of Honshu, is a region of diverse landscapes, ranging from the majestic Japanese Alps to the picturesque Lake Suwa. It is home to numerous traditional crafts, including pottery and textiles, and boasts a rich cultural heritage. Chubu’s strategic location has made it a key transportation hub, connecting the northern and southern parts of Japan.
Kansai: The Cultural Crossroads
Kansai, in western Honshu, is known for its vibrant culture and rich history. Home to the ancient capital of Kyoto, Kansai is a center of traditional arts, including tea ceremonies, Noh theater, and geisha districts. Osaka, the region’s major city, is a bustling commercial hub renowned for its street food and lively atmosphere.
Chugoku: The Land of Mountains and Inland Seas
Chugoku, located in the southwestern part of Honshu, is a region of dramatic mountains, serene inland seas, and historical sites. Its mountainous terrain is dotted with ancient temples and shrines, while its coastline offers picturesque beaches and islands. Chugoku is known for its traditional crafts, such as pottery and textiles, and its rich history, evident in the numerous castles and historical landmarks.
Shikoku: The Island of Pilgrimage
Shikoku, the smallest of the four main islands, is a land of lush forests, rolling hills, and serene mountains. It is renowned for its 88-temple pilgrimage route, a spiritual journey undertaken by many Japanese Buddhists. Shikoku’s coastal areas offer breathtaking views and are known for their fishing communities and traditional crafts.
Kyushu: The Island of Fire and Volcanoes
Kyushu, the southernmost of the four main islands, is a land of volcanic landscapes, hot springs, and vibrant cities. Home to active volcanoes like Mount Aso, Kyushu is known for its geothermal energy and its unique natural beauty. Its diverse culture is influenced by its proximity to mainland Asia, with a strong presence of traditional crafts and local festivals.
The Interconnectedness of Regions
While each region possesses its own unique character, they are interconnected through a shared history, culture, and geography. This interconnectedness is evident in the flow of people, goods, and ideas across the country, shaping the diverse tapestry of Japanese society.
Understanding the Importance of Regional Diversity
Appreciating Japan’s regional map is crucial for understanding the nation’s rich cultural heritage and its diverse landscape. Each region offers a unique perspective on Japanese culture and society, highlighting the country’s multifaceted identity.
FAQs about Japan’s Regional Map
Q: What is the most populous region in Japan?
A: The Kanto region, encompassing Tokyo and its surrounding areas, is the most populous region in Japan.
Q: Which region is known for its traditional crafts?
A: Many regions in Japan are known for their traditional crafts. Tohoku is renowned for its lacquerware, Chubu for its pottery and textiles, Chugoku for its pottery and textiles, and Kyushu for its traditional crafts influenced by its proximity to mainland Asia.
Q: What is the significance of Mount Fuji?
A: Mount Fuji, located in the Kanto region, is a sacred mountain and a symbol of Japan. It is a popular destination for hikers and tourists alike.
Q: Which region is known for its hot springs?
A: Kyushu is known for its hot springs, fueled by its volcanic activity.
Tips for Exploring Japan’s Regions
- Research the specific region you plan to visit. Each region has its unique attractions, cultural experiences, and culinary delights.
- Consider the time of year. Japan’s climate varies significantly across its regions, so plan your trip accordingly.
- Utilize public transportation. Japan’s efficient public transportation system makes it easy to explore different regions.
- Engage with local culture. Take the opportunity to experience traditional festivals, try local cuisine, and interact with local people.
- Learn basic Japanese phrases. Even a few simple phrases can go a long way in enhancing your travel experience.
Conclusion
Japan’s regional map is a testament to the country’s diverse landscape, rich culture, and vibrant history. Understanding the unique characteristics of each region allows for a deeper appreciation of the nation’s multifaceted identity. By exploring the interconnectedness of its regions, travelers can gain a comprehensive understanding of Japan’s intricate tapestry and its enduring spirit.


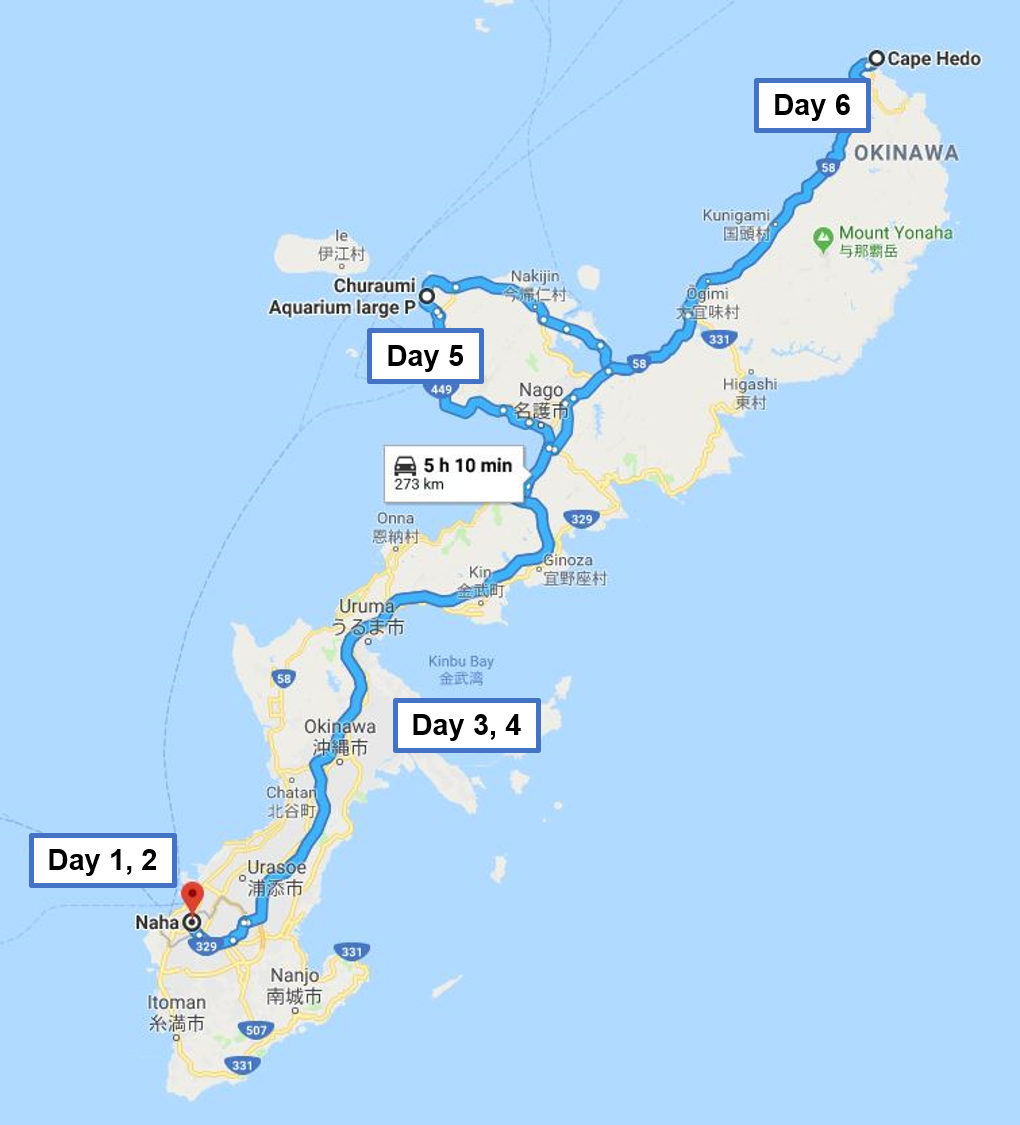
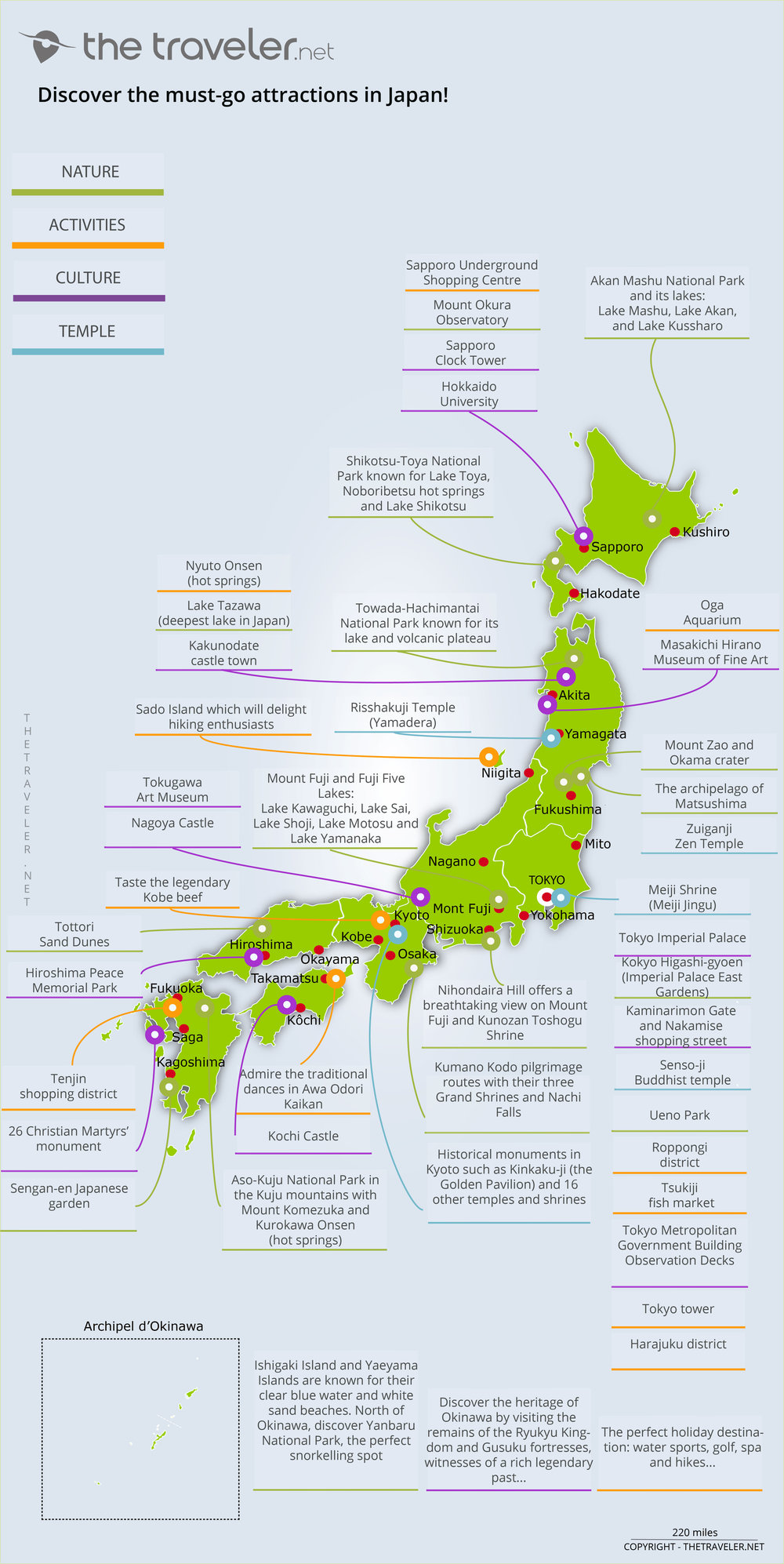

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to Japan’s Regional Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!