Navigating the Waters: Understanding New Jersey’s Flood Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding New Jersey’s Flood Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Waters: Understanding New Jersey’s Flood Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Waters: Understanding New Jersey’s Flood Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Waters: Understanding New Jersey’s Flood Maps
- 3.1 Deciphering the Flood Map: A Visual Guide to Risk
- 3.2 The Importance of Flood Maps: A Crucial Tool for Mitigation and Preparedness
- 3.3 Navigating the Data: A Closer Look at New Jersey’s Flood Risk
- 3.4 Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying the Flood Map
- 3.5 Tips for Utilizing Flood Maps: Making Informed Decisions
- 3.6 Conclusion: Empowering Communities Through Knowledge
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Waters: Understanding New Jersey’s Flood Maps

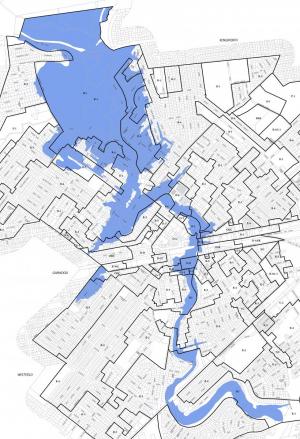
New Jersey, with its extensive coastline and intricate network of rivers and streams, is a state susceptible to flooding. Understanding flood risk is crucial for residents, businesses, and policymakers alike. Flood maps, meticulously crafted by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), serve as essential tools for navigating this risk, providing valuable insights into potential flood zones and their associated hazards.
Deciphering the Flood Map: A Visual Guide to Risk
Flood maps, available online through FEMA’s Flood Map Service Center, are visual representations of flood risk across the state. These maps utilize a standardized color-coding system, with different hues signifying varying degrees of flood hazard. Areas designated as "Special Flood Hazard Areas" (SFHAs) are particularly susceptible to flooding and are subject to specific regulations and insurance requirements.
Understanding the Color Code:
- Blue: Areas with a 1% annual chance of flooding, often referred to as the "100-year floodplain." This means that there is a 1 in 100 chance of flooding in any given year.
- Red: Areas with a 0.2% annual chance of flooding, also known as the "500-year floodplain." This indicates a 1 in 500 chance of flooding in any given year.
- Shaded areas: These represent areas with a lower risk of flooding but are still considered flood-prone.
Beyond the Colors:
Flood maps offer more than just color-coded zones. They also depict:
- Floodway: The portion of a floodplain that must remain unobstructed to allow floodwaters to flow freely.
- Base Flood Elevation (BFE): The elevation of the floodwaters during a 100-year flood event.
- Flood Zones: Specific designations within the SFHA, such as "A" (areas with minimal flood risk) or "V" (areas susceptible to coastal flooding).
The Importance of Flood Maps: A Crucial Tool for Mitigation and Preparedness
Flood maps serve as a vital resource for various stakeholders, informing decisions related to:
- Land Use Planning: Maps help municipalities identify areas susceptible to flooding, guiding development strategies to minimize flood risk and ensure public safety.
- Insurance Policies: Flood insurance, mandatory in SFHAs, is calculated based on flood risk as determined by the maps. Understanding flood zones is crucial for securing appropriate insurance coverage.
- Disaster Preparedness: Maps provide valuable information for emergency planning, enabling communities to prepare for potential flood events and develop effective evacuation strategies.
- Property Valuation: Flood risk significantly impacts property value, and maps provide essential data for accurate assessments.
Navigating the Data: A Closer Look at New Jersey’s Flood Risk
New Jersey’s diverse geography and proximity to the Atlantic Ocean contribute to its vulnerability to various types of flooding:
- Coastal Flooding: Rising sea levels and storm surges pose a significant threat to coastal communities, particularly along the Jersey Shore.
- Riverine Flooding: Heavy rainfall and snowmelt can lead to overflowing rivers, impacting communities located along major waterways like the Delaware River and the Raritan River.
- Tidal Flooding: The combination of high tides and storm surges can cause flooding in coastal areas, particularly during extreme weather events.
Understanding the Specifics:
- Coastal Flood Zones: Areas along the coast are designated as "V" zones, indicating susceptibility to coastal flooding.
- Riverine Flood Zones: Areas along rivers and streams are typically designated as "A" zones, with "A99" indicating a higher flood risk.
- Tidal Flood Zones: Areas influenced by tides are often categorized as "AE" zones, indicating susceptibility to tidal flooding.
Frequently Asked Questions: Demystifying the Flood Map
Q: How can I access the flood map for my property?
A: The FEMA Flood Map Service Center offers an online tool where you can search for your property address and view the associated flood map.
Q: What does it mean if my property is located in an SFHA?
A: If your property is located in an SFHA, you are required to purchase flood insurance if you have a federally backed mortgage. Additionally, certain building and development regulations may apply to your property.
Q: How can I mitigate flood risk on my property?
A: Various strategies can help mitigate flood risk, including elevating structures, installing flood-resistant materials, and implementing landscaping techniques to manage water flow.
Q: What should I do if my property is flooded?
A: In the event of a flood, prioritize safety and evacuate if necessary. Contact your insurance company to report the damage and seek assistance with recovery efforts.
Tips for Utilizing Flood Maps: Making Informed Decisions
- Consult with a professional: A licensed surveyor or engineer can provide expert interpretation of flood maps and offer guidance on flood mitigation strategies.
- Consider the future: Climate change is expected to exacerbate flooding, so it’s essential to consider future flood risk when making property decisions.
- Stay informed: FEMA and local authorities provide updates on flood maps and flood risk assessments. Regularly check for updates and new information.
Conclusion: Empowering Communities Through Knowledge
Flood maps are not just static documents; they are dynamic tools that empower communities to make informed decisions about flood risk. By understanding the information they provide, residents, businesses, and policymakers can take proactive steps to mitigate flood hazards, protect lives and property, and build more resilient communities.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Waters: Understanding New Jersey’s Flood Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!