Unveiling the Hidden Waters: A Comprehensive Look at Aquifer Maps in the United States
Related Articles: Unveiling the Hidden Waters: A Comprehensive Look at Aquifer Maps in the United States
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Hidden Waters: A Comprehensive Look at Aquifer Maps in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Hidden Waters: A Comprehensive Look at Aquifer Maps in the United States
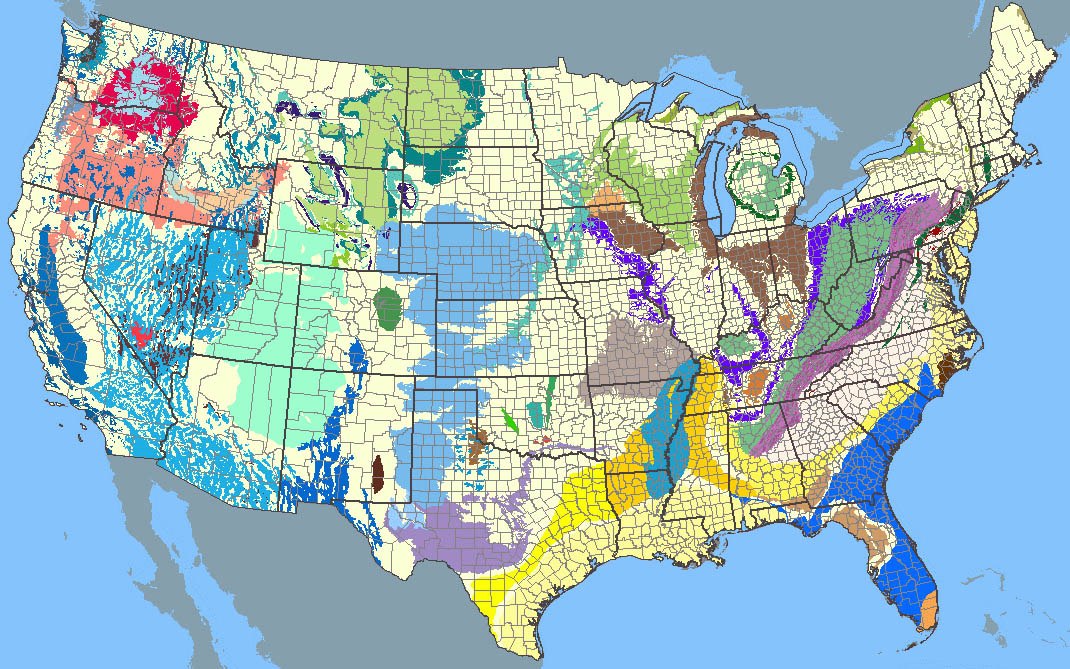
The United States, a vast and diverse nation, relies heavily on its underground water reserves, known as aquifers. These geological formations, often hidden beneath layers of soil and rock, store and transmit water, providing a vital source for agriculture, industry, and domestic use. Understanding the distribution, characteristics, and potential of these aquifers is crucial for sustainable water management. This is where aquifer maps come into play, serving as indispensable tools for water resource planning and decision-making.
Understanding Aquifer Maps: A Window into the Underground
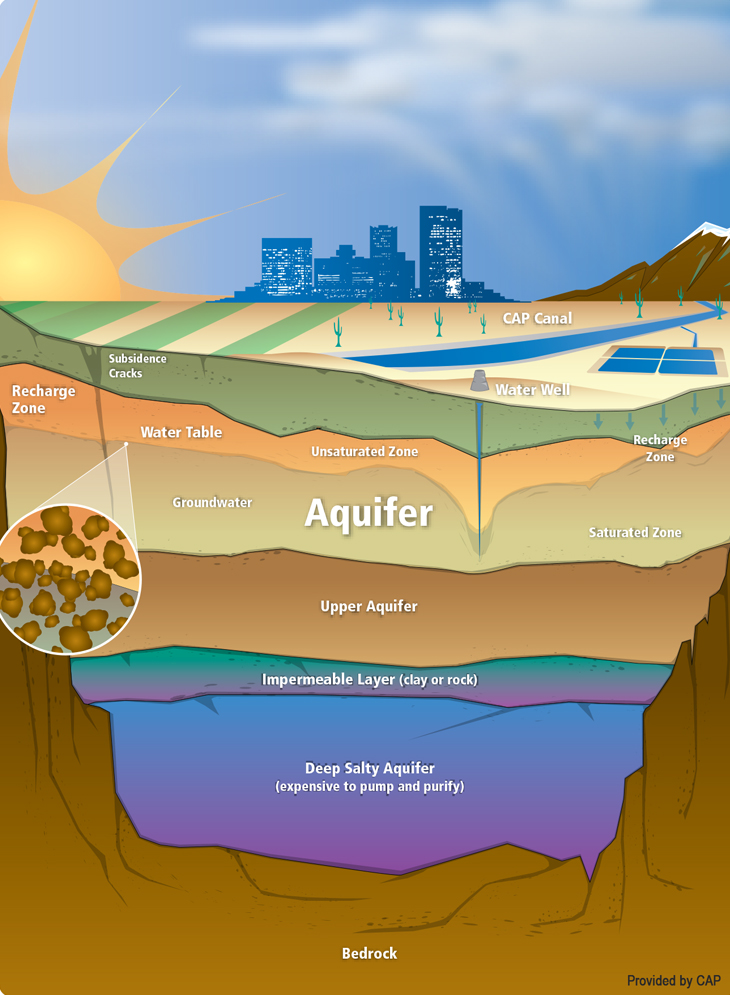
Aquifer maps, in essence, are visual representations of the subsurface, depicting the location, extent, and characteristics of aquifers. These maps provide crucial information about:
- Aquifer Type: Aquifers are classified based on their geological formation and how water is contained within them. Confined aquifers are trapped between layers of impermeable rock, while unconfined aquifers are directly connected to the surface.
- Aquifer Thickness: The thickness of an aquifer determines its storage capacity, influencing the volume of water it can hold.
- Aquifer Yield: This refers to the rate at which an aquifer can release water, influencing its suitability for different uses.
- Aquifer Recharge: This process replenishes aquifers through precipitation, infiltration, and other natural processes.
- Aquifer Vulnerability: Maps often highlight areas where aquifers are more susceptible to contamination from pollutants or saltwater intrusion.
The Importance of Aquifer Maps: Guiding Sustainable Water Management
Aquifer maps serve as a foundation for informed water management decisions, enabling:
- Water Resource Assessment: Maps provide a comprehensive overview of available water resources, helping to identify areas with high or low water availability.
- Water Allocation and Planning: By understanding aquifer characteristics and potential, policymakers can make informed decisions about water allocation for different uses, ensuring equitable distribution and sustainability.
- Groundwater Protection: Aquifer maps help pinpoint areas vulnerable to contamination, enabling the implementation of preventive measures to safeguard groundwater quality.
- Disaster Preparedness: In drought-prone regions, aquifer maps can guide the development of water management strategies for mitigating water shortages.
- Sustainable Development: By understanding the limits and potential of groundwater resources, aquifer maps contribute to sustainable development practices, ensuring the long-term availability of this vital resource.
A Glimpse into the United States Aquifer System: A Diverse Landscape
The United States boasts a diverse array of aquifers, each with its own unique characteristics and potential.
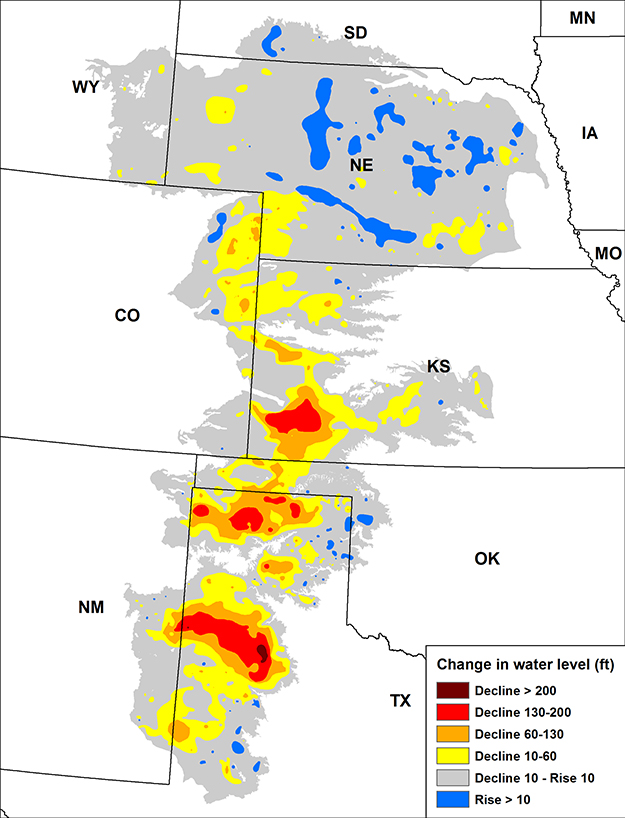
- The High Plains Aquifer: This vast aquifer underlies the Great Plains, spanning eight states. It is a primary source of water for agriculture, but faces challenges due to overpumping and declining water levels.
- The Ogallala Aquifer: A major component of the High Plains Aquifer, the Ogallala provides water for agriculture, livestock, and municipal use. However, it is facing depletion due to intensive agricultural practices.
- The Floridan Aquifer: This vast aquifer underlies parts of Florida, Georgia, Alabama, and South Carolina, supplying water for a range of uses.
- The California Central Valley Aquifer: This aquifer is a critical water source for agriculture in the Central Valley, but is facing challenges due to overpumping and saltwater intrusion.
- The Mississippi River Valley Alluvial Aquifer: This aquifer, stretching from the Mississippi River to the Appalachian Mountains, provides water for agriculture, industry, and municipal use.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Future of Groundwater Management
While aquifer maps provide valuable insights, managing groundwater resources effectively requires addressing a range of challenges:
- Overpumping: Excessive groundwater extraction can lead to aquifer depletion, lowering water tables and potentially causing land subsidence.
- Contamination: Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and sewage can contaminate aquifers, posing risks to human health and ecosystems.
- Climate Change: Climate change can impact aquifer recharge patterns, potentially leading to water scarcity in some regions.
- Data Availability: While progress has been made in developing aquifer maps, data gaps and inconsistencies remain, hindering comprehensive water management.
Addressing these challenges necessitates a multi-pronged approach, including:
- Sustainable Water Use Practices: Promoting water conservation, efficient irrigation techniques, and alternative water sources can reduce reliance on groundwater.
- Groundwater Protection Measures: Implementing regulations to prevent contamination, monitoring water quality, and promoting sustainable land management practices are crucial.
- Investing in Research and Monitoring: Continued research and monitoring efforts are essential to improve our understanding of aquifers and develop effective management strategies.
- Public Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of groundwater and promoting responsible water use are vital for long-term sustainability.
FAQs on Aquifer Maps in the United States
Q: How are aquifer maps created?
A: Aquifer maps are created through a combination of geological surveys, geophysical methods, and data analysis. Geologists use drilling data, well logs, and other geological information to map the location and extent of aquifers. Geophysical techniques, such as seismic surveys and ground penetrating radar, provide insights into the subsurface structure.
Q: Who uses aquifer maps?
A: Aquifer maps are used by a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Water Resource Managers: These professionals rely on maps to assess water availability, plan for water allocation, and manage groundwater resources.
- Environmental Agencies: Aquifer maps help agencies identify and address potential contamination risks, protect groundwater quality, and ensure sustainable water management.
- Farmers and Ranchers: Aquifer maps provide information about groundwater availability, helping farmers and ranchers plan for irrigation and livestock management.
- Researchers and Scientists: Aquifer maps are essential tools for studying groundwater flow, understanding aquifer dynamics, and developing sustainable water management strategies.
Q: Where can I find aquifer maps for my area?
A: Aquifer maps are often available from:
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS is a primary source of aquifer information, providing maps, data, and reports on groundwater resources across the nation.
- State Geological Surveys: Many states have their own geological surveys that collect and disseminate aquifer data for their respective regions.
- Local Water Management Agencies: Local agencies responsible for water management often have aquifer maps and data specific to their jurisdictions.
Q: Are aquifer maps constantly updated?
A: Aquifer maps are dynamic, reflecting changes in groundwater levels, recharge patterns, and other factors. Continuous monitoring and data collection are crucial for updating maps and ensuring their accuracy.
Tips for Using Aquifer Maps Effectively
- Understand the Map’s Purpose: Before using an aquifer map, carefully review its purpose, scale, and intended use.
- Consider Data Limitations: Aquifer maps are based on available data, which may have limitations or inconsistencies.
- Consult with Experts: If you have specific questions or need detailed information, consult with water resource professionals or hydrogeologists.
- Use Multiple Data Sources: Cross-referencing data from different sources, such as geological surveys, well logs, and environmental monitoring reports, can provide a more comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion
Aquifer maps are essential tools for understanding and managing groundwater resources in the United States. They provide a crucial foundation for informed decision-making, enabling sustainable water use, protection of groundwater quality, and effective planning for the future. By leveraging the information provided by these maps, we can ensure the responsible and equitable management of this vital resource, safeguarding its availability for generations to come.
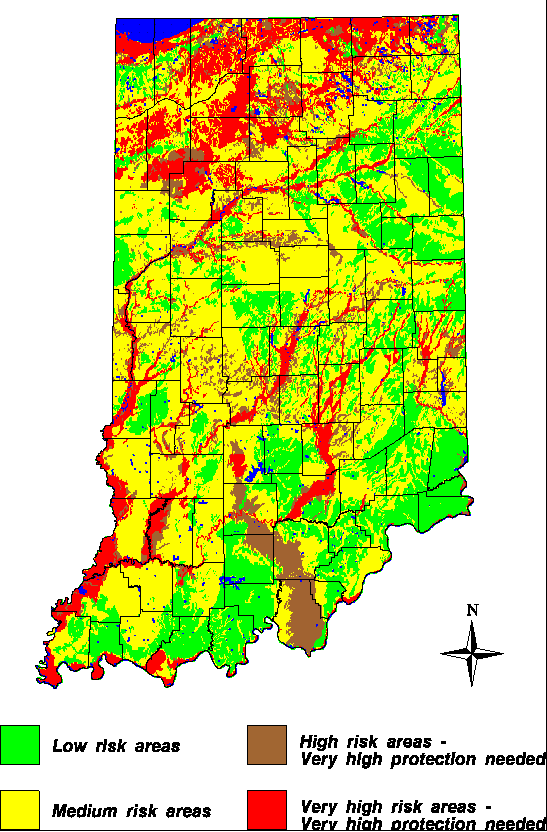
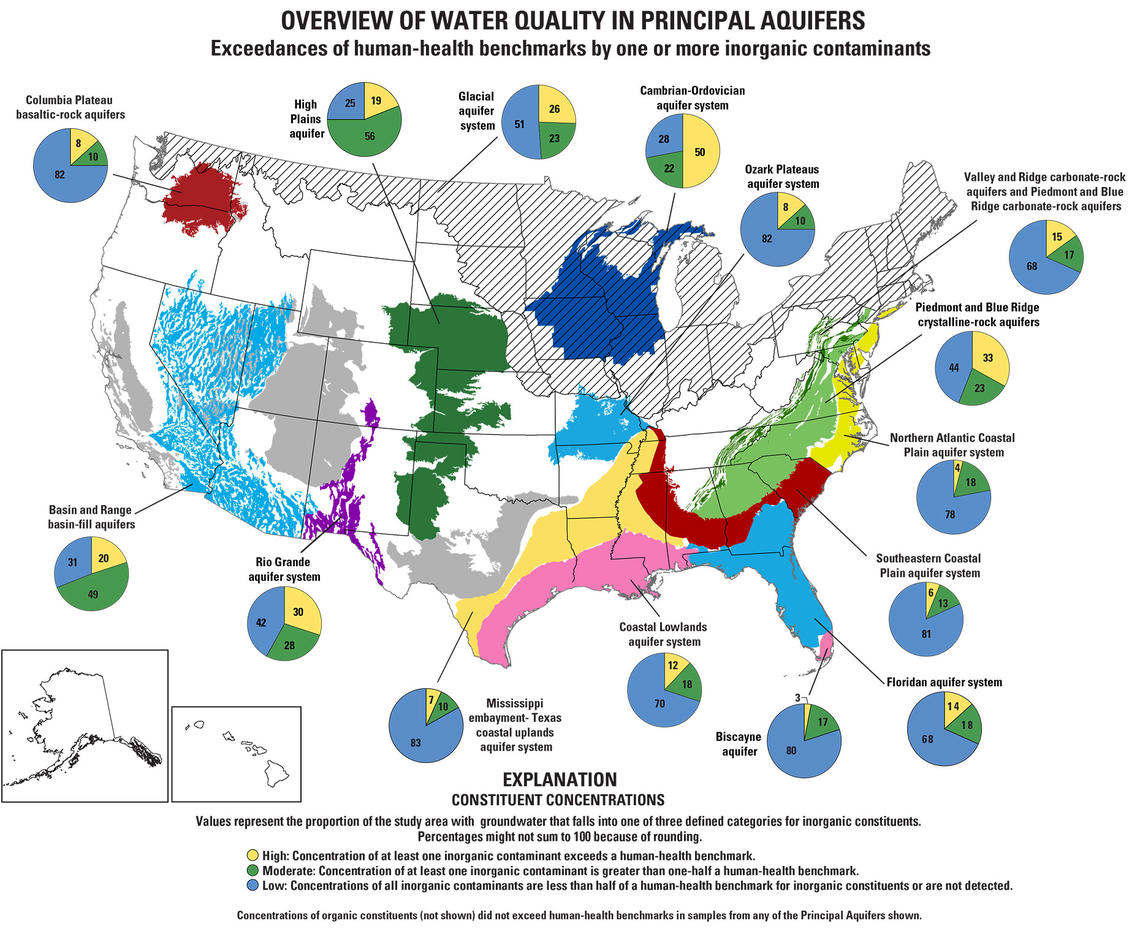

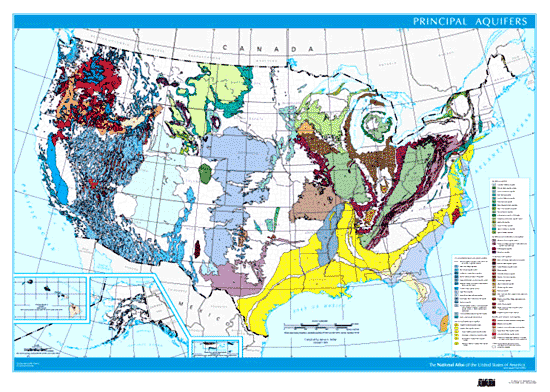


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Hidden Waters: A Comprehensive Look at Aquifer Maps in the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!