Unveiling the Secrets of the Great Basin Desert: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Great Basin Desert: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Great Basin Desert: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Great Basin Desert: A Geographical Exploration

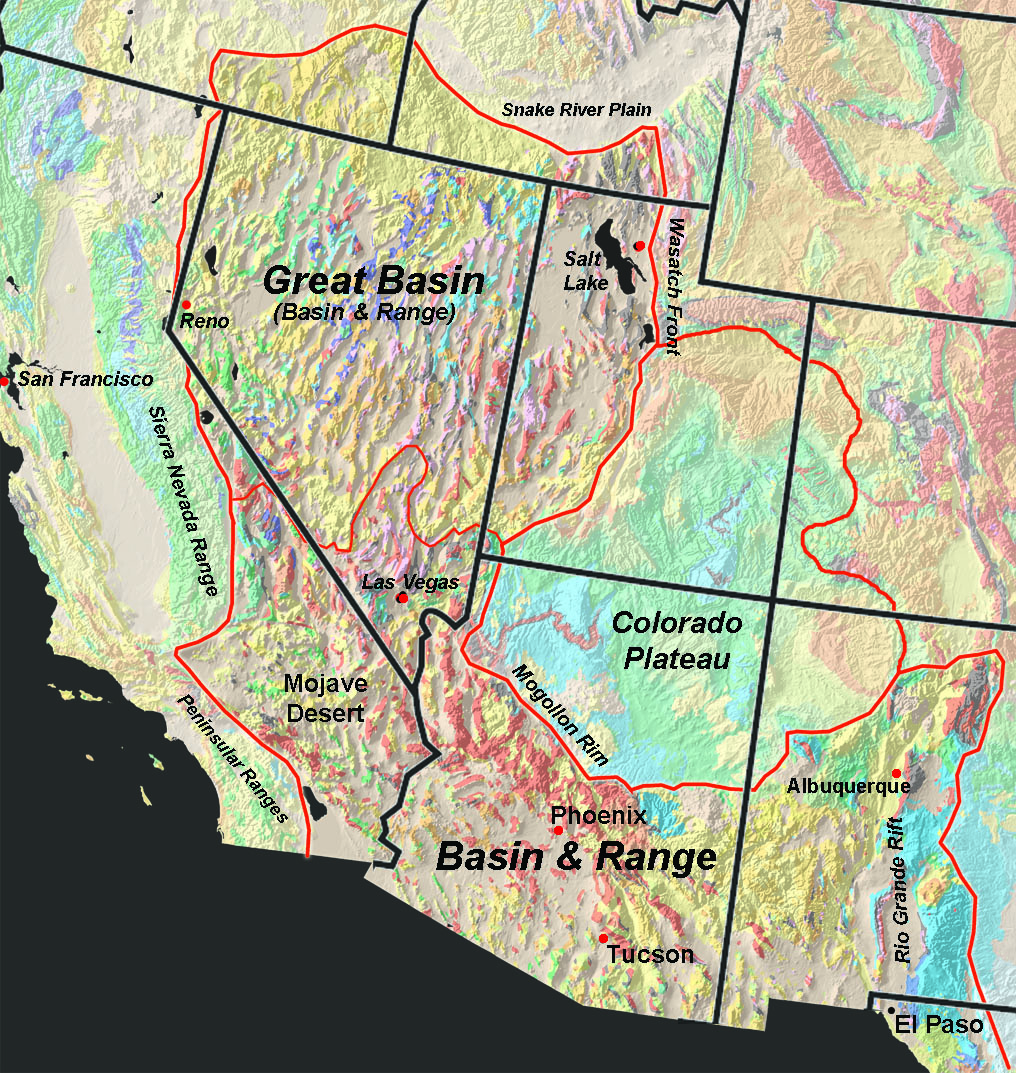
The Great Basin Desert, a vast and arid expanse encompassing much of the western United States, stands as a testament to the resilience of life in extreme environments. Its unique geography, shaped by tectonic forces and the relentless desert climate, has produced a landscape of stark beauty and ecological wonder. Understanding the Great Basin Desert map is crucial for appreciating its ecological significance, its cultural importance, and its potential for human development.
A Journey Through the Basin’s Landscape:
The Great Basin Desert, stretching over 190,000 square miles, encompasses portions of Nevada, Utah, Oregon, California, and Idaho. Its defining characteristic is the presence of numerous closed drainage basins, where water flows inwards but has no outlet to the sea. This creates a unique hydrological system where lakes and rivers are often ephemeral, forming only during periods of heavy rainfall.
The desert’s topography is diverse, featuring rugged mountain ranges interspersed with vast, flat valleys. The Sierra Nevada and the Wasatch Mountains, towering on the western and eastern edges, respectively, cast long shadows across the desert, influencing its climate and shaping its ecosystems. The central portion of the basin is dominated by vast, undulating plains, characterized by sparse vegetation and a seemingly endless horizon.
Geological Forces and the Shaping of the Landscape:
The Great Basin Desert’s geological history is intertwined with the dramatic forces of plate tectonics. Millions of years ago, the North American Plate began to stretch and thin, creating a vast basin that was gradually filled with sediments. Subsequent volcanic activity and uplift formed the mountains that now define the basin’s perimeter.
The ongoing geological activity continues to shape the landscape today. Earthquakes are common, reflecting the ongoing movement of the Earth’s crust. Volcanic activity, though less frequent, has left its mark in the form of cinder cones, lava flows, and calderas, adding to the region’s dramatic and varied topography.
Climate and Adaptation:
The Great Basin Desert is characterized by a cold desert climate, with hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters. The lack of significant rainfall, coupled with high rates of evaporation, creates a challenging environment for life.
Plants and animals have adapted to these extreme conditions in remarkable ways. Plants have evolved deep root systems to access scarce groundwater, while some species have developed water-storing tissues to survive periods of drought. Animals have adapted by becoming nocturnal, minimizing exposure to the intense heat of the day. Others have developed efficient water conservation mechanisms, allowing them to thrive in environments with limited water resources.
Ecological Treasures and Biodiversity:
Despite its harsh conditions, the Great Basin Desert is home to a remarkable array of plant and animal life. The region boasts over 2,000 plant species, including unique species like the bristlecone pine, known for its longevity and resistance to extreme conditions. The desert also supports a diverse fauna, including iconic species like the desert tortoise, the pronghorn antelope, and the Great Basin kangaroo rat.
The Great Basin Desert is also home to several unique ecosystems, including the Great Salt Lake, the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere. The lake provides a critical habitat for migratory birds, brine shrimp, and other aquatic life. The desert’s mountain ranges, with their cooler temperatures and higher precipitation, support forests of pinyon pine and juniper, offering a refuge for a variety of species.
Cultural Significance and Human Impact:
The Great Basin Desert has been inhabited by indigenous peoples for thousands of years. The Paiute, Shoshone, and Washoe tribes, among others, have adapted to the region’s harsh conditions, developing intricate knowledge of its resources and its environment. Their traditional practices, including hunting, gathering, and farming, demonstrate a deep understanding of the delicate balance of the desert ecosystem.
The arrival of European settlers in the 19th century brought significant changes to the Great Basin Desert. Mining, ranching, and agriculture led to the exploitation of the region’s resources, impacting its delicate ecosystem. Today, the desert faces challenges such as habitat fragmentation, invasive species, and climate change, all of which threaten its biodiversity and the livelihoods of the communities that depend on it.
Navigating the Great Basin Desert Map:
The Great Basin Desert map is a valuable tool for understanding the region’s geography, its unique features, and its ecological significance. It reveals the intricate network of mountains, valleys, and rivers that shape the desert’s landscape. It highlights the locations of important natural features, such as national parks, wildlife refuges, and archaeological sites.
The map also provides insights into human activity within the region, including major cities, transportation routes, and areas of economic activity. Understanding the distribution of human settlements and infrastructure is crucial for understanding the impact of human activities on the desert’s ecosystem.
FAQs about the Great Basin Desert Map:
Q: What are the main geographic features of the Great Basin Desert?
A: The Great Basin Desert is characterized by numerous closed drainage basins, rugged mountain ranges, vast flat valleys, and ephemeral lakes and rivers.
Q: What are the major mountain ranges within the Great Basin Desert?
A: The Sierra Nevada, the Wasatch Mountains, the Snake Range, and the White Mountains are some of the major mountain ranges that define the Great Basin Desert’s perimeter.
Q: What are the major cities located within the Great Basin Desert?
A: Some of the major cities located within the Great Basin Desert include Las Vegas, Salt Lake City, Reno, and Boise.
Q: What are the major ecological threats facing the Great Basin Desert?
A: The Great Basin Desert faces threats such as habitat fragmentation, invasive species, climate change, and overgrazing.
Q: What are some of the unique plant and animal species found in the Great Basin Desert?
A: The Great Basin Desert is home to unique species such as the bristlecone pine, the desert tortoise, the pronghorn antelope, and the Great Basin kangaroo rat.
Tips for Exploring the Great Basin Desert Map:
- Use a variety of resources: Utilize online maps, topographic maps, and atlases to gain a comprehensive understanding of the Great Basin Desert.
- Focus on specific features: Explore the map to identify key features such as mountain ranges, valleys, rivers, and lakes.
- Consider the scale: Adjust the map’s scale to focus on specific areas of interest or to view the broader regional context.
- Identify human impact: Observe the distribution of human settlements, transportation routes, and areas of economic activity to understand the impact of human activities on the desert’s ecosystem.
Conclusion:
The Great Basin Desert, with its unique geography, harsh climate, and rich biodiversity, stands as a testament to the resilience of life in extreme environments. Understanding the Great Basin Desert map is essential for appreciating its ecological significance, its cultural importance, and its potential for human development. By navigating the map, we can gain insights into the region’s natural wonders, its challenges, and the need for responsible stewardship of this remarkable landscape.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Great Basin Desert: A Geographical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!