Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Mesoamerica: A Comparative Look at the Aztec and Mayan Empires
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Mesoamerica: A Comparative Look at the Aztec and Mayan Empires
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Mesoamerica: A Comparative Look at the Aztec and Mayan Empires. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Mesoamerica: A Comparative Look at the Aztec and Mayan Empires

The vibrant civilizations of the Aztecs and Mayans, flourishing in Mesoamerica between the 14th and 16th centuries, continue to captivate the imagination. Their intricate societal structures, impressive architectural achievements, and sophisticated cultural practices leave an indelible mark on history. To fully appreciate the scope and complexity of these civilizations, it is crucial to understand their geographical footprint – their empires. This article delves into the distinct geographical realms of the Aztecs and Mayans, highlighting the unique characteristics of their respective territories and the profound influence these landscapes had on their civilizations.
The Aztec Empire: A Realm of Power and Control
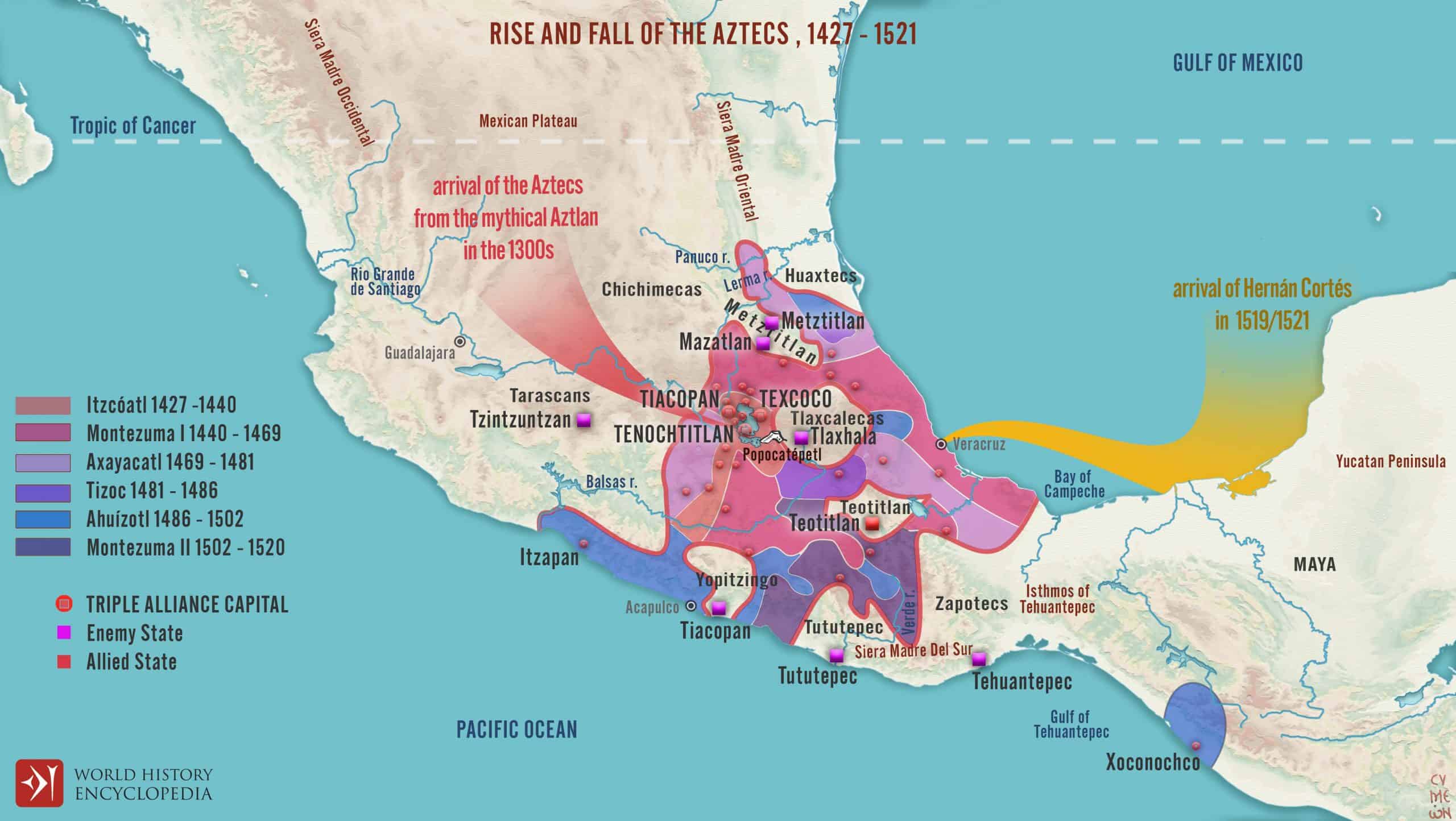
The Aztec Empire, centered around the Valley of Mexico, was a formidable force in Mesoamerica. Its influence extended far beyond its core territory, encompassing vast swathes of land from central Mexico to Guatemala. The empire’s strategic location in the Valley of Mexico, a fertile basin surrounded by mountains, provided access to abundant resources, including water, fertile land, and natural resources. The valley’s location also facilitated trade and communication with other regions, contributing to the empire’s economic and political strength.
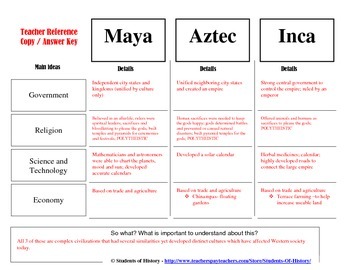
The Aztecs’ dominance was cemented by their military prowess and a sophisticated system of governance. They established a complex network of alliances and tributaries, effectively controlling a vast network of city-states and territories. The empire’s expansive territory was divided into provinces, each governed by a local ruler who owed allegiance to the Aztec emperor. This system of centralized control allowed the Aztecs to maintain order and extract resources from their conquered territories.
The Mayan Civilization: A Mosaic of City-States
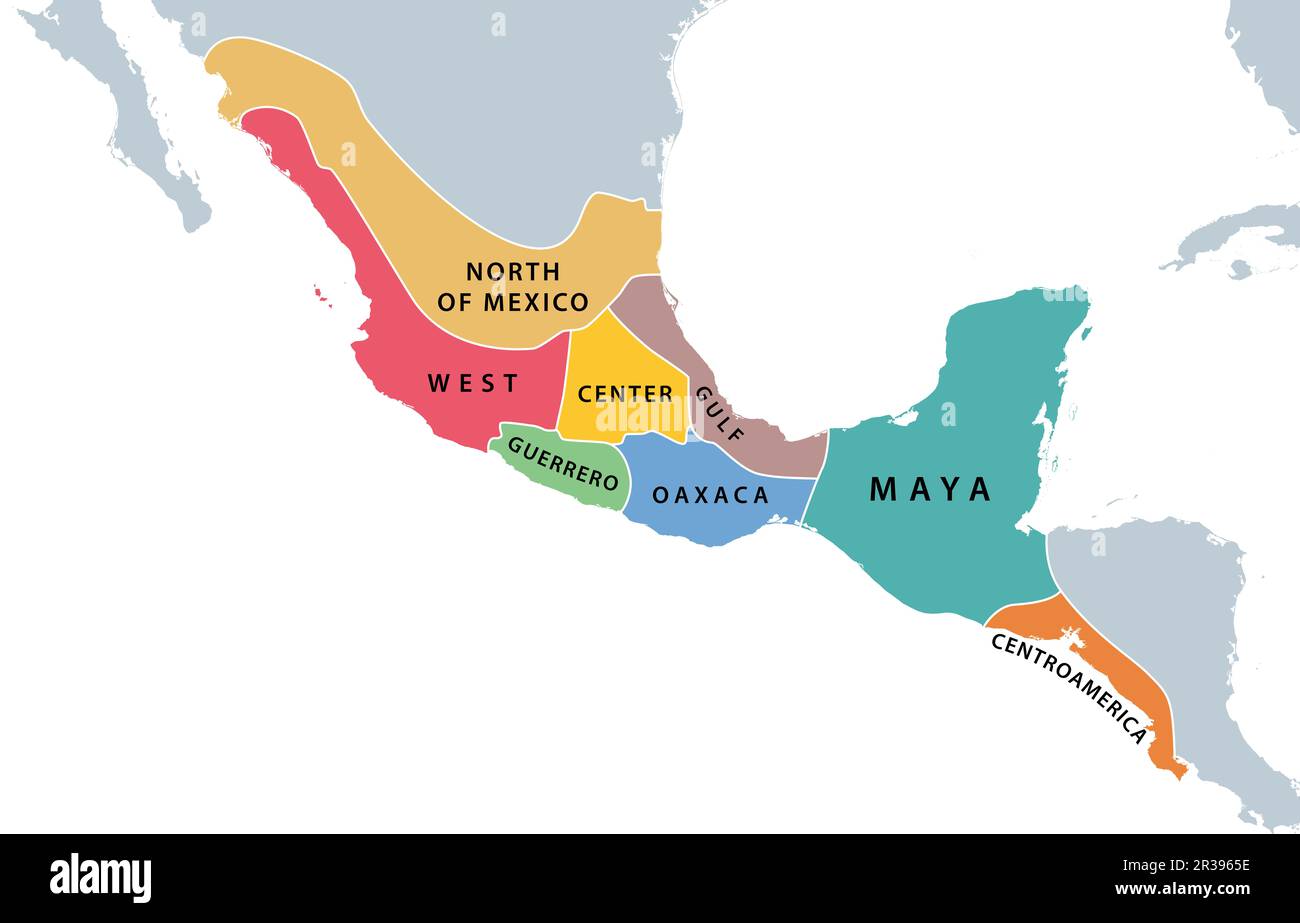
Unlike the centralized Aztec Empire, the Mayan civilization was characterized by a decentralized structure, with numerous independent city-states scattered across a vast region encompassing present-day southeastern Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras, and El Salvador. This dispersed settlement pattern was largely influenced by the region’s diverse topography, which included lush rainforests, rugged mountains, and fertile lowlands.
The Maya city-states developed their own distinct cultures and traditions, often engaging in trade and diplomacy while also competing for resources and political influence. This decentralized structure fostered a vibrant and diverse cultural landscape, characterized by distinct artistic styles, architectural innovations, and religious practices. The Mayan civilization’s enduring legacy lies in its sophisticated calendar system, complex hieroglyphic writing, and impressive architectural achievements, including monumental pyramids, temples, and palaces.
Comparing the Empires: A Tale of Two Landscapes
The geographical differences between the Aztec and Mayan empires had a profound impact on their respective civilizations. The Aztecs, situated in the fertile Valley of Mexico, developed an agricultural system that relied heavily on irrigation and terracing. Their empire’s location provided access to a rich diversity of resources, including obsidian, salt, and precious metals, which fueled their economic growth and military power.
The Mayans, on the other hand, adapted to a more diverse and challenging landscape. Their civilization flourished in regions characterized by dense rainforests, fertile lowlands, and rugged mountains. This diverse environment influenced their agricultural practices, leading to the development of sophisticated techniques like slash-and-burn agriculture and raised fields. The Mayans also harnessed the power of the natural world, utilizing the abundant rainfall to cultivate crops and build elaborate irrigation systems.
The Importance of Understanding the Geographical Context
Understanding the geographical context of the Aztec and Mayan empires is crucial for appreciating the complexities of their civilizations. The empires’ geographical locations, resources, and environmental challenges played a pivotal role in shaping their political structures, economic systems, cultural practices, and ultimately, their destinies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What were the major geographical features of the Aztec Empire?
A: The Aztec Empire was centered in the Valley of Mexico, a fertile basin surrounded by mountains. The valley’s location provided access to abundant resources, including water, fertile land, and natural resources. The empire also controlled vast swathes of land from central Mexico to Guatemala.
Q: How did the Mayans adapt to their diverse environment?
A: The Mayans developed sophisticated agricultural practices, including slash-and-burn agriculture and raised fields, to adapt to the diverse environment of their region. They also utilized the abundant rainfall to cultivate crops and build elaborate irrigation systems.
Q: What were the major differences between the Aztec and Mayan empires in terms of their political structures?
A: The Aztec Empire was highly centralized, with a powerful emperor and a complex system of governance. The Mayan civilization, on the other hand, was characterized by a decentralized structure, with numerous independent city-states scattered across a vast region.
Q: What is the significance of understanding the geographical context of ancient civilizations?
A: Understanding the geographical context of ancient civilizations is crucial for appreciating the complexities of their societies. The empires’ geographical locations, resources, and environmental challenges played a pivotal role in shaping their political structures, economic systems, cultural practices, and ultimately, their destinies.
Tips for Further Exploration
- Explore online maps: Interactive online maps can provide a detailed visualization of the Aztec and Mayan empires, highlighting their geographical boundaries, major cities, and important geographical features.
- Visit museums and archaeological sites: Museums and archaeological sites offer a tangible connection to the past, showcasing artifacts, architectural remnants, and cultural expressions of the Aztec and Mayan civilizations.
- Read books and articles: There are numerous books and articles available that delve into the history, culture, and geography of the Aztec and Mayan empires. These resources can provide a deeper understanding of their civilizations and their place in Mesoamerican history.
Conclusion
The geographical realms of the Aztec and Mayan empires were not simply static backdrops for their civilizations but active participants in their development. The empires’ unique landscapes shaped their political structures, economic systems, cultural practices, and ultimately, their destinies. By understanding the geographical context of these ancient civilizations, we gain a richer appreciation for their complexities, resilience, and enduring legacies. The study of these empires continues to offer valuable insights into the human capacity for adaptation, innovation, and cultural expression, reminding us of the interconnectedness of civilizations and the enduring power of place.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Ancient Mesoamerica: A Comparative Look at the Aztec and Mayan Empires. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!