Unveiling the West: A Geographic Exploration of the United States
Related Articles: Unveiling the West: A Geographic Exploration of the United States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the West: A Geographic Exploration of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the West: A Geographic Exploration of the United States

The Western United States, a region encompassing a vast expanse of land from the Rocky Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, boasts a diverse tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and industries. Understanding the geography of this region is crucial for appreciating its natural wonders, its historical significance, and its impact on the nation’s economy and society.
Defining the West:
While there is no universally accepted definition of the Western United States, it generally encompasses the following states:
- Pacific Coast: California, Oregon, Washington
- Rocky Mountain States: Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, Idaho, Nevada
- Southwest: Arizona, New Mexico
- Great Plains States: North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas (often considered part of the Midwest, but share significant geographic and cultural ties with the West)
A Land of Contrasts:
The West is a region of striking contrasts, characterized by:
- Vast Landscapes: From towering mountain ranges like the Sierra Nevada and the Rockies to arid deserts like the Mojave and the Sonoran, the West encompasses a wide variety of terrains.
- Diverse Climates: The region experiences a range of climates, from the temperate rainforests of the Pacific Northwest to the scorching deserts of the Southwest.
- Abundant Natural Resources: The West is rich in natural resources, including timber, minerals, oil, and natural gas.
- Cultural Diversity: The West has been shaped by a diverse range of cultures, including Native American, Hispanic, Asian, and European influences.
Geographic Features and their Significance:
1. The Rocky Mountains:
- Geological Formation: The Rocky Mountains, a majestic range extending from Canada to New Mexico, were formed by tectonic plate collisions millions of years ago.
- Importance: The Rockies are a vital source of water for the West, with numerous rivers originating in the high peaks and flowing eastward and westward. They are also a major tourist destination, offering opportunities for hiking, skiing, and other outdoor recreation.
2. The Great Basin:
- Geological Formation: The Great Basin, a vast, arid region located between the Sierra Nevada and the Rocky Mountains, is characterized by its internal drainage system, meaning that its rivers do not flow to the ocean.
- Importance: The Great Basin is home to a unique ecosystem, with adapted plants and animals that thrive in the harsh desert conditions. It also contains valuable mineral deposits, including gold and silver.
3. The Pacific Coast:
- Geological Formation: The Pacific Coast is shaped by the Pacific Plate, which is constantly moving and interacting with the North American Plate. This interaction has resulted in the formation of the San Andreas Fault, a major source of seismic activity.
- Importance: The Pacific Coast is a vital economic engine for the West, with major industries including agriculture, tourism, and technology. It is also home to some of the nation’s largest cities, including Los Angeles, San Francisco, and Seattle.
4. The Colorado River:
- Geological Formation: The Colorado River, a major river system that flows through the Southwest, originates in the Rocky Mountains and empties into the Gulf of California.
- Importance: The Colorado River is a critical source of water for millions of people in the Southwest, providing irrigation for agriculture and drinking water for cities. It is also a popular destination for boating, fishing, and rafting.
Historical Significance:
The West played a pivotal role in the expansion of the United States, shaping its history and identity.
- Native American Culture: The West was once home to a diverse array of Native American cultures, each with its own unique traditions, languages, and ways of life.
- Exploration and Settlement: European explorers and settlers began venturing into the West in the 16th century, seeking new lands, resources, and opportunities.
- The Gold Rush: The discovery of gold in California in 1848 sparked a massive influx of people, transforming the region and driving its economic growth.
- Frontier Life: The West was a place of hardship and adventure, where pioneers faced challenges such as harsh weather, disease, and conflict with Native Americans.
- Western Expansion: The westward expansion of the United States was a defining period in American history, shaping the nation’s political landscape and its sense of national identity.
Economic Importance:
The West remains a vital economic engine for the United States, contributing significantly to the nation’s GDP and employing millions of people.
- Agriculture: The West is a major agricultural producer, growing crops such as wheat, corn, cotton, and fruits and vegetables.
- Energy: The West is a major source of energy, producing oil, natural gas, coal, and hydroelectric power.
- Tourism: The West’s stunning natural beauty attracts millions of tourists each year, generating revenue for the region’s economy.
- Technology: The West is a hub for the technology industry, with major companies such as Google, Apple, and Microsoft headquartered in the region.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The West faces a number of challenges, including:
- Water Scarcity: The West is a water-scarce region, with growing demands for water from agriculture, industry, and urban areas.
- Climate Change: Climate change is impacting the West, with increased temperatures, drought, and wildfire risks.
- Environmental Degradation: Development and resource extraction have led to environmental degradation in some areas of the West.
However, the West also presents a number of opportunities:
- Renewable Energy: The West has significant potential for renewable energy, such as solar and wind power.
- Innovation: The West is a hub for innovation, with a thriving technology sector and a culture of entrepreneurship.
- Conservation: There are growing efforts to conserve the West’s natural resources and ecosystems.
FAQs about the Western United States Map:
1. What is the largest state in the Western United States?
The largest state in the Western United States is Alaska, although it is often considered part of the Northwest region rather than the contiguous West. However, if we consider only the contiguous states, the largest is California.
2. What is the most populated state in the Western United States?
The most populated state in the Western United States is California, with a population exceeding 39 million.
3. What are the major mountain ranges in the Western United States?
The major mountain ranges in the Western United States include the Rocky Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, the Cascade Range, the Coast Mountains, and the Appalachian Mountains (although the Appalachian Mountains are primarily located in the Eastern United States, a small portion extends into the Western United States).
4. What are the major rivers in the Western United States?
The major rivers in the Western United States include the Colorado River, the Columbia River, the Snake River, the Rio Grande River, and the Sacramento River.
5. What are the major cities in the Western United States?
The major cities in the Western United States include Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle, Denver, Phoenix, San Diego, Portland, Las Vegas, Salt Lake City, and Albuquerque.
Tips for Understanding the Western United States Map:
- Use a detailed map: A detailed map of the Western United States will help you identify the various states, cities, and geographic features.
- Study the physical features: Pay attention to the major mountain ranges, rivers, and deserts.
- Research the history: Learn about the historical events that shaped the West, such as the Gold Rush and the westward expansion.
- Explore the culture: Discover the diverse cultures that have shaped the West, including Native American, Hispanic, Asian, and European influences.
- Travel and experience: There is no better way to understand the West than to travel and experience it firsthand.
Conclusion:
The Western United States is a region of immense beauty, rich history, and economic significance. Understanding its geography, its history, and its challenges and opportunities is crucial for appreciating its role in the nation’s development and for shaping its future. The Western United States map provides a valuable tool for exploring and understanding this fascinating region.

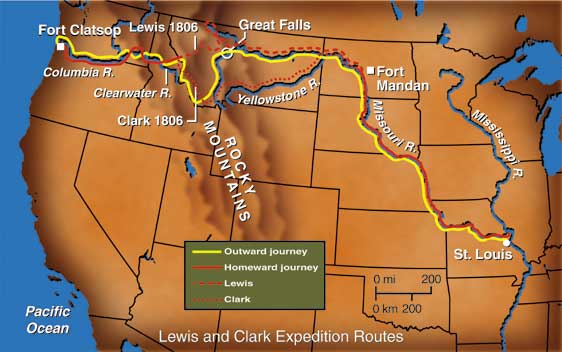

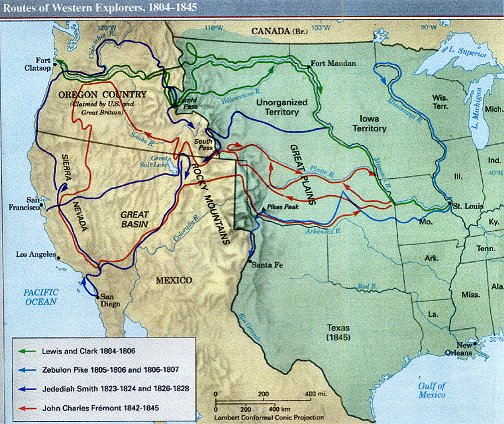


![Exploration: Lewis and Clark [ushistory.org]](https://www.ushistory.org/us/images/lewclark.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the West: A Geographic Exploration of the United States. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!