A Regional Atlas of Europe: Unveiling the Continent’s Numerous Tapestry
Associated Articles: A Regional Atlas of Europe: Unveiling the Continent’s Numerous Tapestry
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we are going to discover the intriguing subject associated to A Regional Atlas of Europe: Unveiling the Continent’s Numerous Tapestry. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
A Regional Atlas of Europe: Unveiling the Continent’s Numerous Tapestry

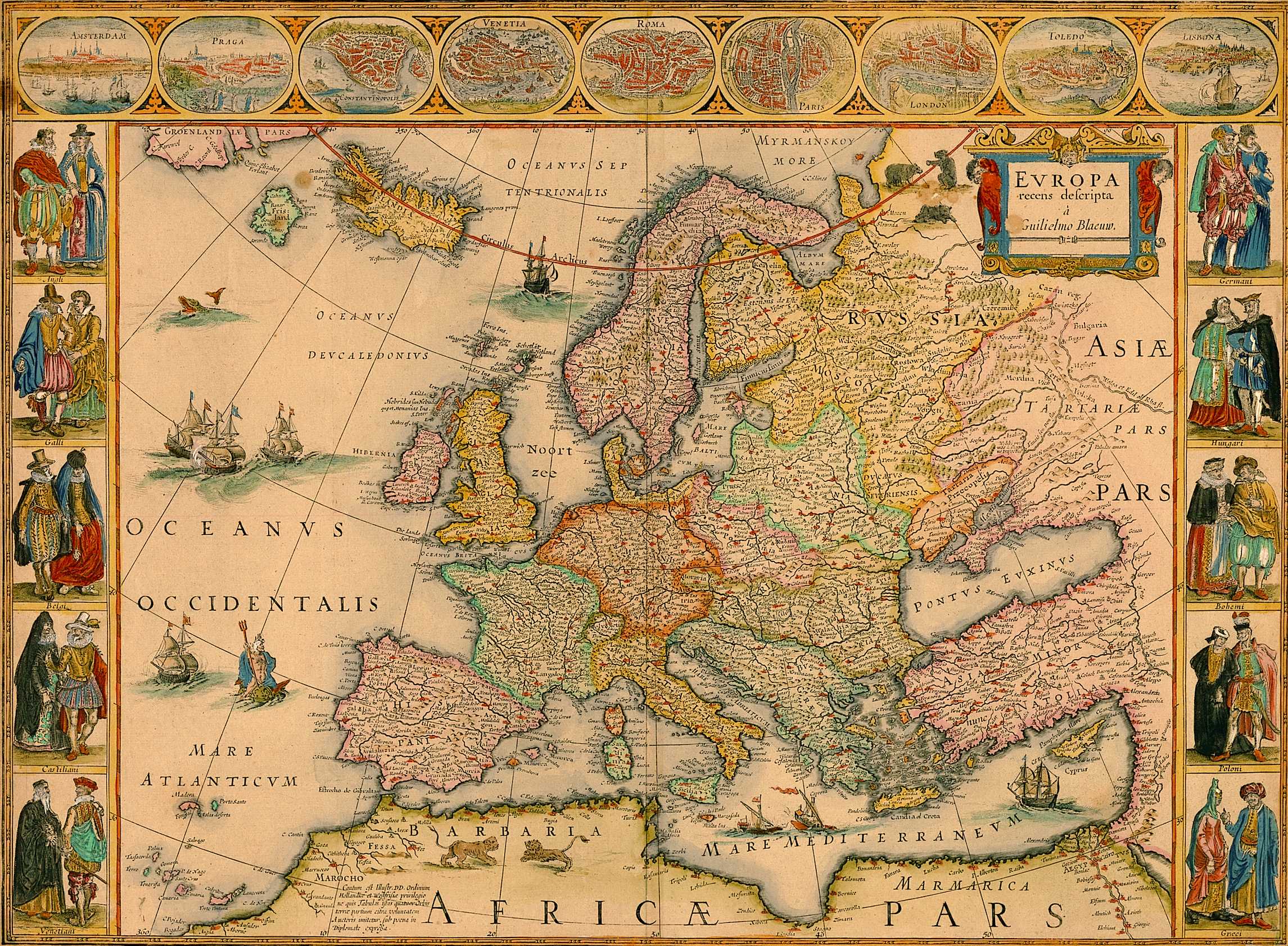
Europe, a continent steeped in historical past, tradition, and political intrigue, is way from a monolithic entity. Its various panorama, formed by millennia of migration, conquest, and cultural alternate, is greatest understood by way of a regional lens. This text will discover a regional division of Europe, analyzing the geographical, historic, and cultural nuances that outline every space. Whereas any regional division is inherently subjective, this map goals to offer a complete overview, acknowledging the complexities and overlaps inherent in such a classification.
I. Northern Europe: A Realm of Fjords and Fjells
Northern Europe, encompassing Scandinavia (Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland, Iceland), and sometimes together with the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania), is characterised by its rugged landscapes, lengthy coastlines, and comparatively sparse inhabitants. The Scandinavian international locations share a historical past rooted in Viking seafaring, a legacy mirrored of their maritime traditions and societal buildings. Norway’s dramatic fjords, Sweden’s huge forests, and Finland’s numerous lakes create a singular surroundings, formed by the lengthy, darkish winters and brief, vibrant summers. Iceland, an island nation characterised by volcanic exercise and geothermal power, stands aside with its distinctive geological formations and vibrant cultural heritage.
The Baltic states, having spent many years below Soviet rule, have since embraced independence and integration into the European Union. Their historical past, nevertheless, stays interwoven with that of their bigger neighbors, Russia and Germany, leading to a definite cultural mix. The area’s economies are more and more targeted on know-how and innovation, whereas sustaining sturdy ties to their conventional industries, similar to forestry and fishing.
Key Traits of Northern Europe:
- Dominant Landscapes: Fjords, forests, lakes, tundra.
- Historic Influences: Viking Age, Lutheranism, Nordic Council cooperation.
- Financial Focus: Know-how, renewable power, forestry, fishing.
- Cultural Traits: Sturdy social security nets, emphasis on egalitarianism, nature conservation.
II. Western Europe: The Coronary heart of the European Union
Western Europe, typically thought-about the "core" of the European Union, encompasses a various vary of nations, together with France, Germany, the UK, the Benelux international locations (Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg), Eire, and typically Portugal and Spain. This area has been a crucible of European historical past, witnessing the rise and fall of empires, the event of democracy, and the beginning of the trendy nation-state. The area is characterised by excessive inhabitants densities, superior economies, and vital cultural affect globally.
France, with its wealthy historical past and cultural heritage, stays a significant participant in European affairs. Germany, Europe’s largest financial system, performs an important function within the EU’s political and financial panorama. The UK, regardless of its latest departure from the EU, continues to exert vital world affect. The Benelux international locations, recognized for his or her worldwide enterprise and commerce, are necessary hubs for European commerce. Eire, with its vibrant tech sector, has skilled vital financial development in latest many years. Portugal and Spain, whereas geographically positioned on the Iberian Peninsula, share many cultural and historic ties with Western Europe, significantly by way of their shared historical past with the Roman Empire.
Key Traits of Western Europe:
- Dominant Landscapes: Coastal plains, rolling hills, river valleys.
- Historic Influences: Roman Empire, Renaissance, Enlightenment, Industrial Revolution.
- Financial Focus: Superior manufacturing, finance, know-how, tourism.
- Cultural Traits: Cosmopolitanism, various languages and cultures, sturdy emphasis on particular person liberties.
III. Central Europe: A Crossroads of Cultures
Central Europe, a area typically outlined by its geographical location between Western and Japanese Europe, contains international locations similar to Germany (partially), Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Austria, Slovenia, and typically Switzerland and Liechtenstein. This area has a fancy and sometimes turbulent historical past, marked by durations of each prosperity and battle. The area’s location on the crossroads of varied empires, together with the Holy Roman Empire, Austro-Hungarian Empire, and the Soviet Union, has left a long-lasting impression on its cultural panorama.
The area boasts a wealthy architectural heritage, reflecting centuries of inventive and cultural growth. Central Europe’s historical past can be marked by vital spiritual and ethnic range, resulting in each durations of concord and battle. At present, these international locations are largely built-in into the European Union, although they proceed to navigate their distinctive historic legacies.
Key Traits of Central Europe:
- Dominant Landscapes: Plains, mountains, river basins.
- Historic Influences: Holy Roman Empire, Habsburg Monarchy, Communism, post-Soviet transition.
- Financial Focus: Manufacturing, automotive business, tourism.
- Cultural Traits: Mix of Western and Japanese European influences, wealthy folks traditions.
IV. Japanese Europe: A Area in Transition
Japanese Europe, encompassing international locations similar to Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria, Serbia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Kosovo, Albania, and typically the Baltic states, has a historical past deeply intertwined with the Soviet Union. The area skilled many years of communist rule, adopted by a interval of dramatic political and financial transformation after the autumn of the Berlin Wall. This transition has been marked by vital challenges, together with financial instability, political corruption, and ethnic tensions.
Japanese Europe’s various panorama ranges from the Carpathian Mountains to the Black Beach. The area’s cultural heritage is a mix of Slavic, Byzantine, and Ottoman influences. At present, many Japanese European international locations are members of the European Union and NATO, looking for nearer integration with the West whereas grappling with their distinctive post-Soviet realities.
Key Traits of Japanese Europe:
- Dominant Landscapes: Plains, mountains, Black Beach.
- Historic Influences: Ottoman Empire, Russian Empire, Soviet Union, post-Soviet transition.
- Financial Focus: Agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, rising service sectors.
- Cultural Traits: Sturdy nationwide identities, various spiritual traditions, ongoing efforts towards democratic consolidation.
V. Southern Europe: A Mediterranean Mosaic
Southern Europe, encompassing Italy, Greece, Spain (partially), Portugal (partially), Malta, Cyprus, and typically components of France and Croatia, is outlined by its Mediterranean local weather, shoreline, and wealthy historical past. This area has been a cradle of civilization, dwelling to historic empires such because the Roman and Greek civilizations. The area’s panorama is characterised by sun-drenched coastlines, rolling hills, and mountainous terrain.
Southern Europe’s economies are closely reliant on tourism, agriculture, and more and more, know-how and repair industries. The area’s cultural heritage is a vibrant tapestry of historic and trendy influences, reflecting centuries of interplay with completely different cultures and civilizations. Whereas dealing with financial challenges, the area continues to be a significant vacationer vacation spot and a big cultural contributor to the European panorama.
Key Traits of Southern Europe:
- Dominant Landscapes: Mediterranean shoreline, mountains, rolling hills.
- Historic Influences: Roman Empire, Greek civilization, Ottoman Empire.
- Financial Focus: Tourism, agriculture, know-how, service industries.
- Cultural Traits: Sturdy emphasis on household and neighborhood, vibrant inventive traditions, Mediterranean way of life.
Conclusion:
This regional division of Europe serves as a place to begin for understanding the continent’s intricate tapestry of cultures, histories, and landscapes. It’s essential to keep in mind that these areas should not rigidly outlined, and vital overlaps and nuances exist. Nonetheless, by contemplating these regional groupings, we are able to achieve a deeper appreciation for the variety and complexity of Europe and its ongoing evolution. Additional analysis into the person international locations and sub-regions inside every class will reveal much more fascinating particulars about this dynamic and influential continent.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied helpful insights into A Regional Atlas of Europe: Unveiling the Continent’s Numerous Tapestry. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!