Madagascar: An Island Big on the World Map
Associated Articles: Madagascar: An Island Big on the World Map
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Madagascar: An Island Big on the World Map. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Madagascar: An Island Big on the World Map
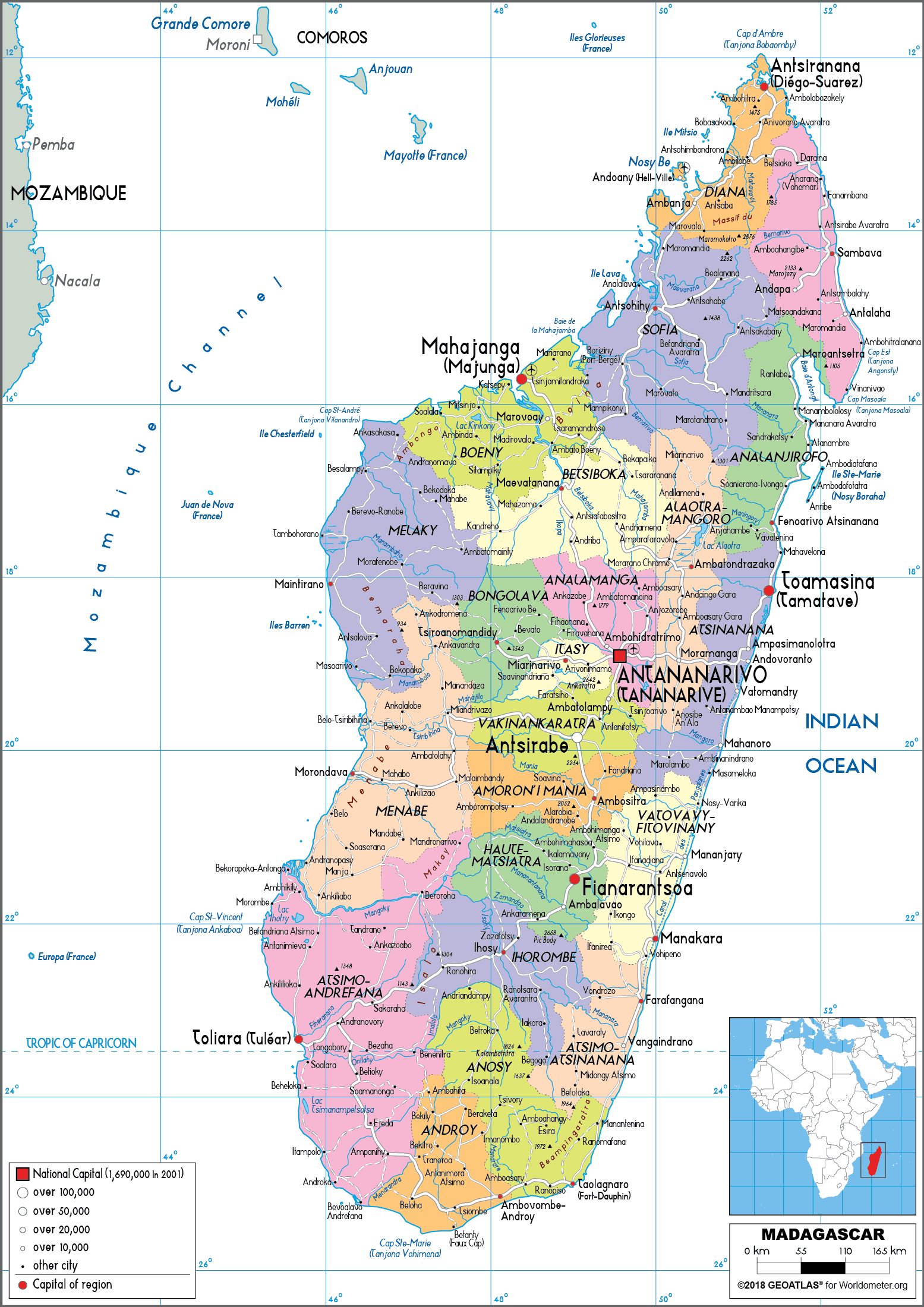
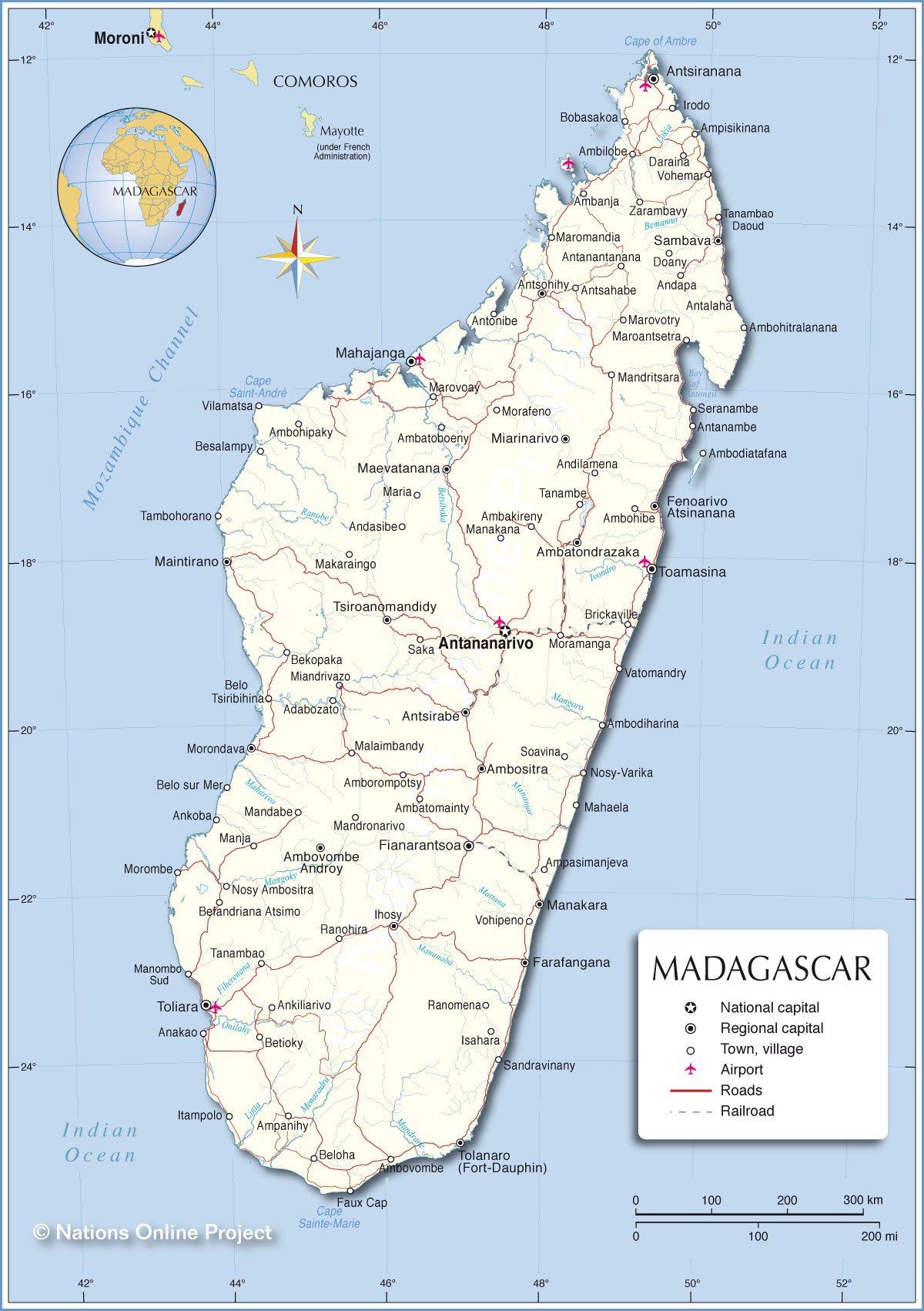
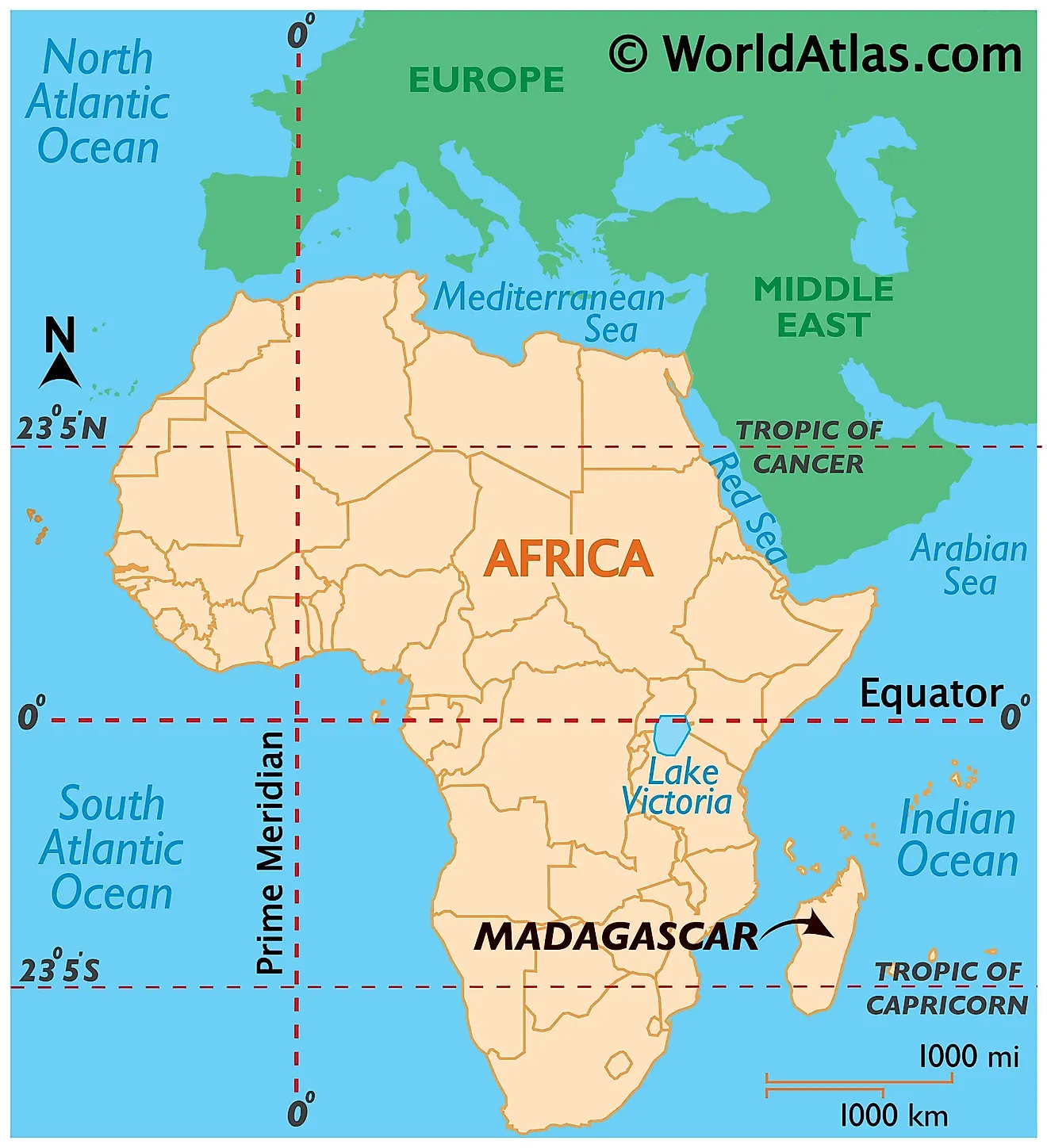
Madagascar, the fourth-largest island on the planet, sits proudly off the southeastern coast of Africa, a jewel within the Indian Ocean. Its distinctive place on the world map has profoundly formed its geography, biodiversity, and tradition, making a nation in contrast to every other. This text delves into the island’s geographical significance, its wealthy pure heritage, its complicated socio-political panorama, and its essential function within the international ecosystem.
Geographical Significance: A Continent in Miniature
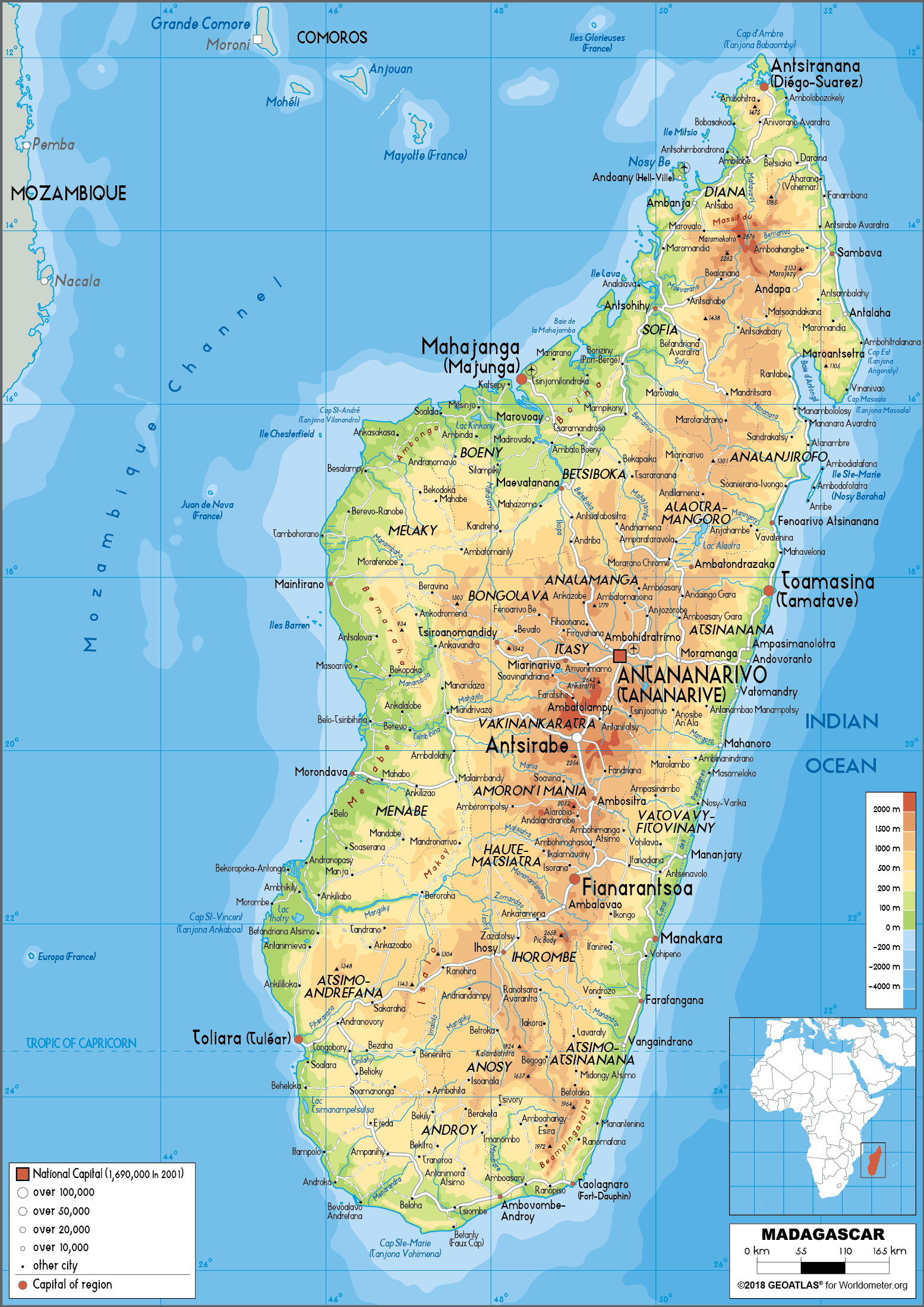
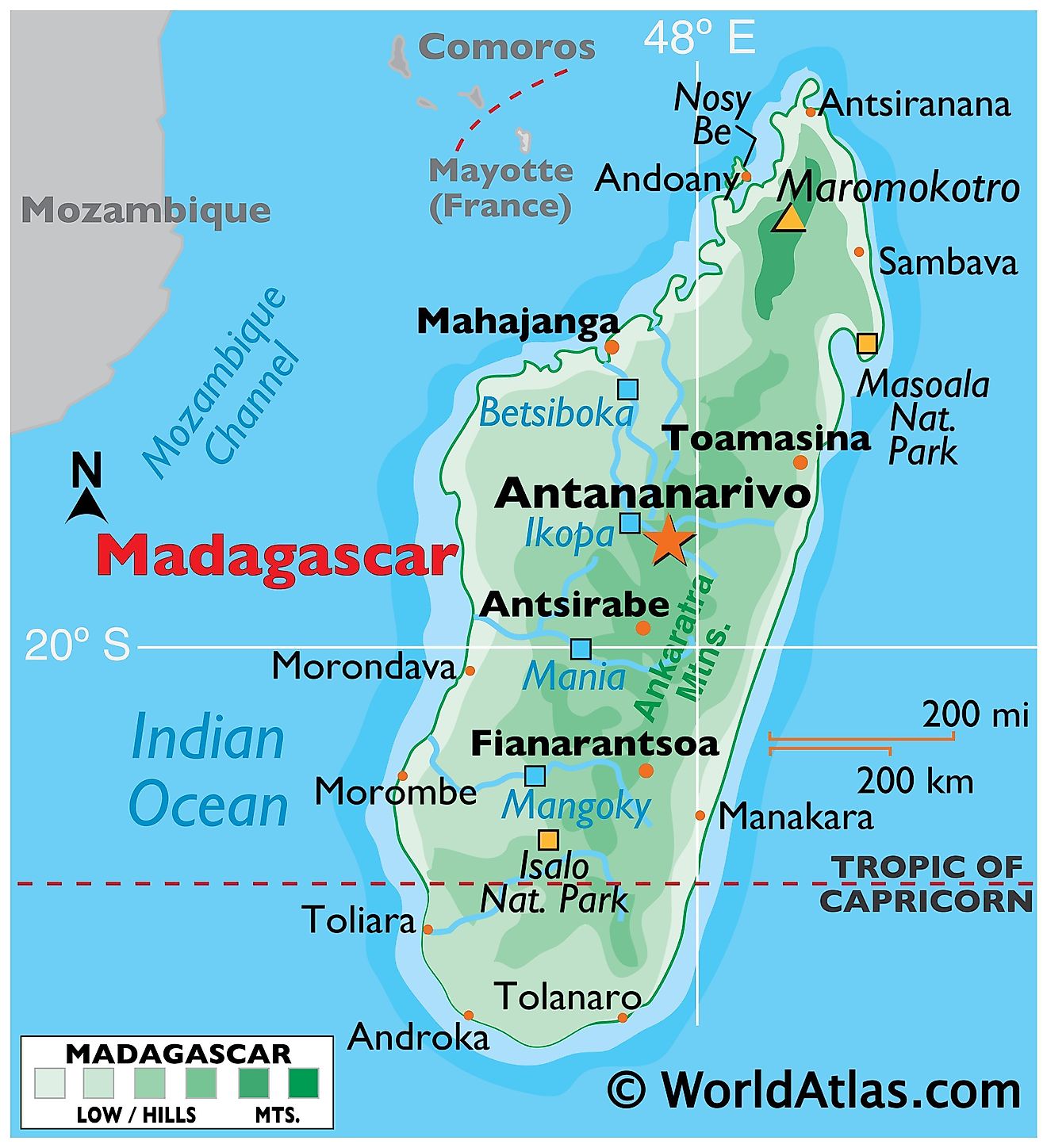
Madagascar’s location, separated from the African mainland by the Mozambique Channel, is its defining attribute. This isolation, spanning hundreds of thousands of years, has fostered the evolution of a very outstanding ecosystem, teeming with endemic species discovered nowhere else on Earth. The island’s measurement – roughly 587,000 sq. kilometers – permits for an enormous variety of habitats, starting from lush rainforests and arid deserts to towering granite massifs and expansive coastal plains. This geographical variety is mirrored in its diverse climates, starting from tropical within the north and east to extra temperate situations within the central highlands and drier climates within the south and west.
The island’s geological historical past is equally fascinating. Initially a part of the supercontinent Gondwana, Madagascar separated from India round 88 million years in the past, initiating a protracted interval of isolation. This geological separation, coupled with the island’s numerous topography, has resulted in a singular evolutionary trajectory, resulting in the spectacular biodiversity for which it’s famend. The central highlands, fashioned by historic volcanic exercise, dominate the island’s panorama, influencing rainfall patterns and shaping the distribution of wildlife. The quite a few rivers originating in these highlands carve their technique to the coast, creating fertile valleys and contributing to the island’s agricultural potential.
The island’s shoreline is intensive and diverse, that includes beautiful seashores, mangrove forests, and coral reefs. These coastal ecosystems are essential for fishing and tourism, two important sectors of the Malagasy economic system. The Mozambique Channel, whereas separating Madagascar from Africa, additionally acts as a significant maritime freeway, connecting the island to the worldwide commerce community. Its strategic location has traditionally made Madagascar a focus for commerce and migration, influencing its cultural variety.
Biodiversity Hotspot: A Treasure Trove of Endemic Species
Madagascar is globally acknowledged as a biodiversity hotspot, boasting an astonishing degree of endemism. Over 80% of its plant and animal species are discovered nowhere else on Earth. This distinctive biodiversity is a testomony to the island’s lengthy isolation and its numerous habitats. Lemurs, the island’s iconic primates, are a chief instance of this distinctive evolution. With over 100 species and subspecies, lemurs exhibit an unimaginable variety in measurement, conduct, and habitat preferences. Many lemur species are critically endangered, highlighting the pressing want for conservation efforts.
Past lemurs, Madagascar is house to a outstanding array of endemic species, together with chameleons (the best variety globally), tenrecs (spiny mammals), fossa (a big carnivorous mammal), and an enormous array of birds, reptiles, amphibians, and bugs. The island’s distinctive flora consists of baobab bushes, numerous orchids, and a wealthy number of medicinal crops. This distinctive biodiversity contributes considerably to the island’s ecological and financial worth, providing alternatives for ecotourism and the event of pure merchandise. Nevertheless, this wealthy biodiversity is beneath immense strain from habitat loss, deforestation, and unlawful wildlife commerce.
Socio-Political Panorama: A Nation in Transition
Madagascar’s socio-political panorama is complicated and dynamic. A historical past marked by colonial rule, political instability, and financial challenges has formed the nation’s present trajectory. The island’s numerous ethnic teams, every with its personal distinctive traditions and customs, contribute to a wealthy cultural tapestry however have additionally, at instances, fueled social tensions. The Malagasy persons are predominantly ethnically numerous, with varied teams talking totally different dialects of Malagasy and French. This linguistic variety displays the island’s wealthy historical past and its publicity to exterior influences.
The nation’s economic system is closely reliant on agriculture, with subsistence farming dominating the agricultural panorama. Whereas possessing vital pure assets, together with minerals and tourism potential, Madagascar faces vital challenges when it comes to poverty, infrastructure improvement, and governance. Political instability has hampered financial development and hindered efforts to handle social inequalities. Nevertheless, current years have witnessed makes an attempt at political reform and financial diversification, aiming to create a extra secure and affluent future.
International Significance: Conservation and Growth Challenges
Madagascar’s international significance extends past its distinctive biodiversity and cultural heritage. The island performs a vital function in regulating the worldwide local weather, performing as a carbon sink and supporting important marine ecosystems. The safety of Madagascar’s forests is essential for mitigating local weather change and preserving biodiversity. Nevertheless, deforestation continues to be a significant risk, pushed by agricultural enlargement, logging, and mining actions.
The worldwide group acknowledges the significance of supporting Madagascar’s conservation efforts. Quite a few worldwide organizations and NGOs are working in partnership with the Malagasy authorities to guard endangered species, fight deforestation, and promote sustainable improvement. Ecotourism performs a significant function in producing income for conservation initiatives and offering financial alternatives for native communities. The problem lies in balancing the wants of financial improvement with the crucial of environmental safety.
Conclusion: A Future for Madagascar
Madagascar’s place on the world map is not only geographical; it’s a reflection of its distinctive place within the international ecosystem and its wealthy cultural heritage. The island’s biodiversity is a treasure trove of pure wonders, however it’s beneath immense strain. Addressing the challenges of poverty, political instability, and environmental degradation is essential for guaranteeing a sustainable future for Madagascar. By fostering collaboration between the Malagasy authorities, worldwide organizations, and native communities, it’s doable to safeguard this outstanding island’s biodiversity, promote sustainable improvement, and safe its rightful place as a worldwide chief in conservation and cultural preservation. The way forward for Madagascar is inextricably linked to the worldwide group’s dedication to supporting its distinctive journey in the direction of a affluent and sustainable future. Its continued existence as a thriving ecosystem and a culturally wealthy nation is determined by the collective efforts to guard its invaluable pure and cultural heritage for generations to come back.
Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered invaluable insights into Madagascar: An Island Big on the World Map. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!