Mapping the Controversy: A Detailed Have a look at the Nord Stream 2 Pipeline
Associated Articles: Mapping the Controversy: A Detailed Have a look at the Nord Stream 2 Pipeline
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing subject associated to Mapping the Controversy: A Detailed Have a look at the Nord Stream 2 Pipeline. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Controversy: A Detailed Have a look at the Nord Stream 2 Pipeline

The Nord Stream 2 pipeline, a controversial mission accomplished in September 2021, represents a major geopolitical and financial growth in Europe. Its building, operation, and supreme destiny are intertwined with advanced energy dynamics, power safety issues, and environmental concerns. Understanding the pipeline’s geographical route is essential to appreciating its implications. This text will present an in depth examination of the Nord Stream 2 pipeline map, analyzing its path, key infrastructure factors, and the geopolitical implications of its location.
The Pipeline’s Route: A Direct Line to Dependence?
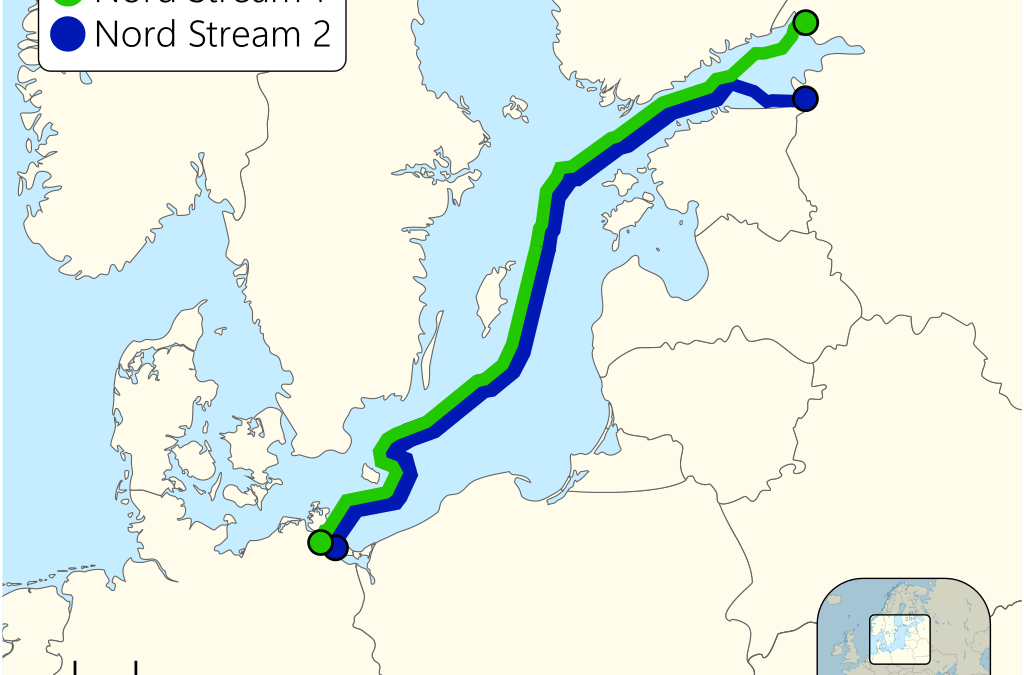
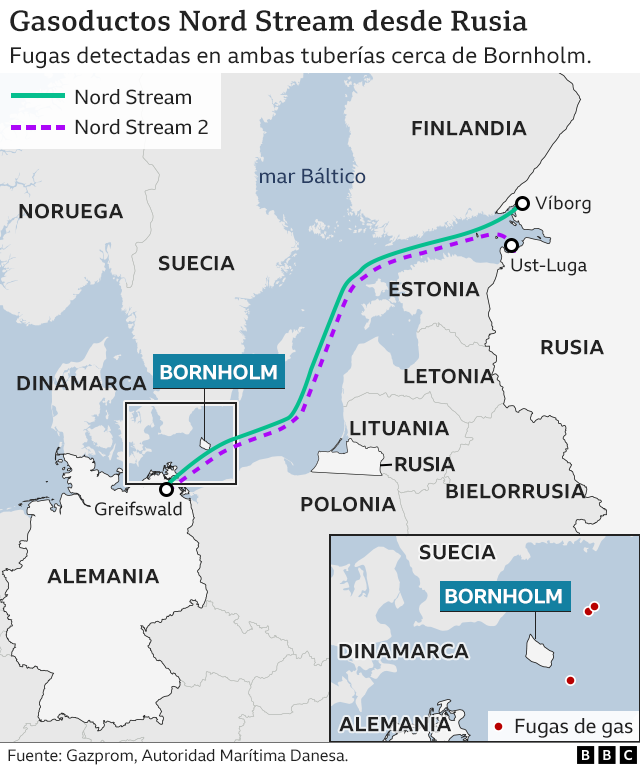
Nord Stream 2, a twin pipeline operating parallel to the prevailing Nord Stream 1, stretches roughly 1,230 kilometers (764 miles) throughout the Baltic Sea. Its route begins in Ust-Luga, Russia, a strategically essential port close to St. Petersburg, and terminates in Greifswald, Germany, a serious German port on the Baltic coast. Not like the southern route of different main fuel pipelines that transit by way of a number of Japanese European international locations, Nord Stream 2’s direct path avoids these transit states completely. This direct route is a key aspect within the controversy surrounding the mission.
Key Geographic Options and Infrastructure:
The pipeline’s trajectory throughout the Baltic Sea necessitates navigating numerous geographical options and environmental concerns. The route passes by way of the unique financial zones (EEZs) of Russia, Finland, Sweden, Denmark, and Germany. Every of those international locations performed a vital function within the allowing and regulatory processes, contributing to the protracted and infrequently contentious nature of the mission’s growth.
-
Ust-Luga, Russia: The place to begin represents a crucial hub for Russian fuel exports. Its location supplies direct entry to the huge fuel fields of Western Siberia, facilitating the environment friendly transport of pure fuel to the pipeline. The port’s infrastructure is particularly designed to deal with the logistical calls for of such a large-scale mission.
-
Baltic Sea Crossing: The vast majority of the pipeline’s size traverses the Baltic Sea, a comparatively shallow and ecologically delicate physique of water. The development course of required cautious consideration of environmental impression assessments, together with the potential results on marine life and seabed habitats. The pipeline’s depth varies alongside its route, requiring specialised engineering and building strategies to make sure its stability and integrity. This part is especially susceptible to potential sabotage or unintentional harm.
-
Danish Unique Financial Zone: The pipeline’s passage by way of the Danish EEZ was significantly contentious. Denmark, conscious of its environmental issues and geopolitical positioning, imposed stringent regulatory necessities and environmental impression assessments. The Danish authorities’s approval was a major milestone within the mission’s completion.
-
Greifswald, Germany: The terminal level in Greifswald connects to the German pure fuel grid, offering direct entry to the European market. Greifswald’s location facilitates the distribution of fuel to numerous components of Germany and, by way of interconnected pipelines, to different European international locations. The presence of this terminal underscores Germany’s important dependence on Russian fuel, a dependence that has been closely criticized for the reason that begin of the warfare in Ukraine.
Geopolitical Implications of the Pipeline’s Route:
The Nord Stream 2 pipeline’s route considerably impacts the geopolitical panorama of Europe. By bypassing Ukraine and different transit international locations, the pipeline reduces the leverage these international locations maintain over Russian fuel transit charges. This has been seen by some as a strategic transfer by Russia to avoid these international locations and improve its affect over the European power market. The direct route additionally reduces transit prices for Russia, making its fuel extra aggressive within the European market.
The mission’s completion has considerably elevated Germany’s dependence on Russian fuel, an element that critics argue undermines European power safety and will increase vulnerability to Russian geopolitical strain. This dependence grew to become acutely obvious following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, when Russia weaponized its power provides, resulting in important worth will increase and power insecurity throughout Europe.
Environmental Issues and the Pipeline’s Route:
The pipeline’s building has raised substantial environmental issues, significantly concerning its potential impression on the Baltic Sea ecosystem. The laying of the pipeline throughout the seabed might probably disrupt marine habitats, have an effect on fish migration patterns, and improve the danger of methane leaks. Whereas environmental impression assessments have been performed, the potential long-term ecological penalties stay a topic of debate and ongoing monitoring.
The pipeline’s vulnerability to unintentional harm or sabotage additionally poses an environmental threat. A significant leak might have devastating penalties for the marine surroundings, resulting in widespread air pollution and ecological harm. The pipeline’s location in a comparatively shallow sea additional enhances this threat.
The Pipeline’s Present Standing and Future Uncertainties:
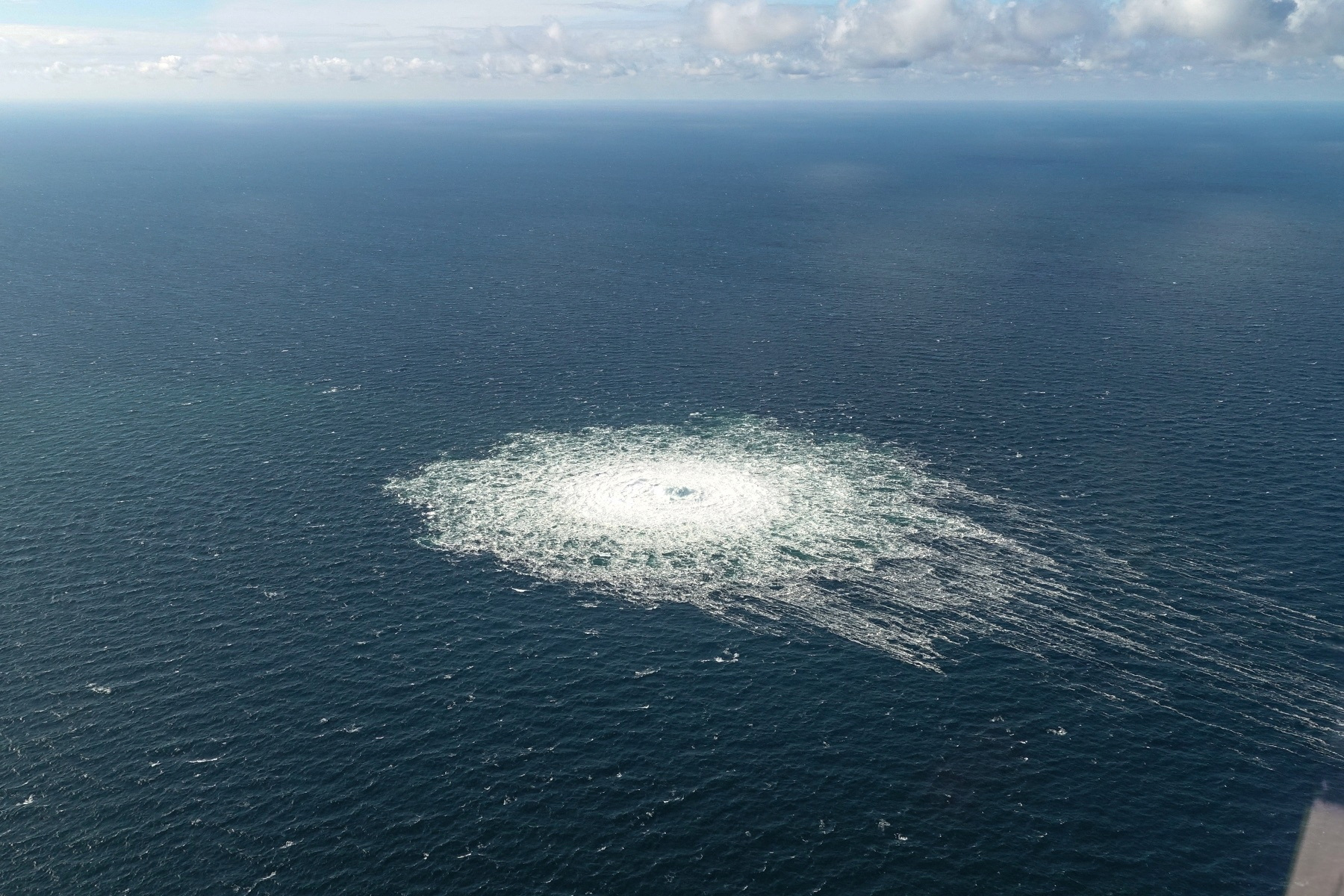
Following the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, the Nord Stream 2 pipeline was successfully halted. Whereas technically accomplished, the German authorities suspended its certification course of, successfully stopping its operation. Subsequently, each Nord Stream 1 and Nord Stream 2 pipelines suffered important harm in September 2022, leading to huge leaks of pure fuel into the Baltic Sea. Investigations into the reason for the harm are ongoing, with accusations of sabotage being levied in opposition to numerous actors.
The way forward for Nord Stream 2 stays extremely unsure. Given the geopolitical tensions and the environmental harm brought on by the leaks, it’s unlikely that the pipeline shall be operational within the foreseeable future. The incident highlights the vulnerability of main power infrastructure to geopolitical instability and the potential environmental penalties of such initiatives.
Conclusion: A Map of Complexities
The Nord Stream 2 pipeline map is greater than only a geographical illustration; it is a visible depiction of advanced geopolitical, financial, and environmental interactions. The pipeline’s direct route, its passage by way of delicate ecological zones, and its impression on European power safety all contribute to its controversial legacy. The pipeline’s present state, following the sabotage incidents, underscores the intertwined nature of power politics, worldwide relations, and environmental issues within the twenty first century. The map serves as a stark reminder of the far-reaching penalties of large-scale power infrastructure initiatives and the necessity for cautious consideration of their geopolitical, financial, and environmental implications. The evaluation of this map ought to function a vital instrument for understanding the evolving power panorama of Europe and the continued challenges associated to power safety and sustainability.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Mapping the Controversy: A Detailed Have a look at the Nord Stream 2 Pipeline. We admire your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!