Pokémon GO Map: Google Maps, Ingress, and the Augmented Actuality Panorama
Associated Articles: Pokémon GO Map: Google Maps, Ingress, and the Augmented Actuality Panorama
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by the intriguing matter associated to Pokémon GO Map: Google Maps, Ingress, and the Augmented Actuality Panorama. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Pokémon GO Map: Google Maps, Ingress, and the Augmented Actuality Panorama

Pokémon GO, the augmented actuality (AR) cell sport that swept the globe in 2016, would not exist with out a refined understanding and utilization of real-world mapping knowledge. Whereas the sport itself does not straight use Google Maps in the best way a typical navigation app may, its underlying infrastructure closely depends on mapping know-how, primarily drawing from Niantic’s personal Ingress platform and its by-product datasets. This text delves into the complicated relationship between Pokémon GO, Google Maps, and the broader world of AR mapping.
The Basis: Ingress and its Knowledge Legacy
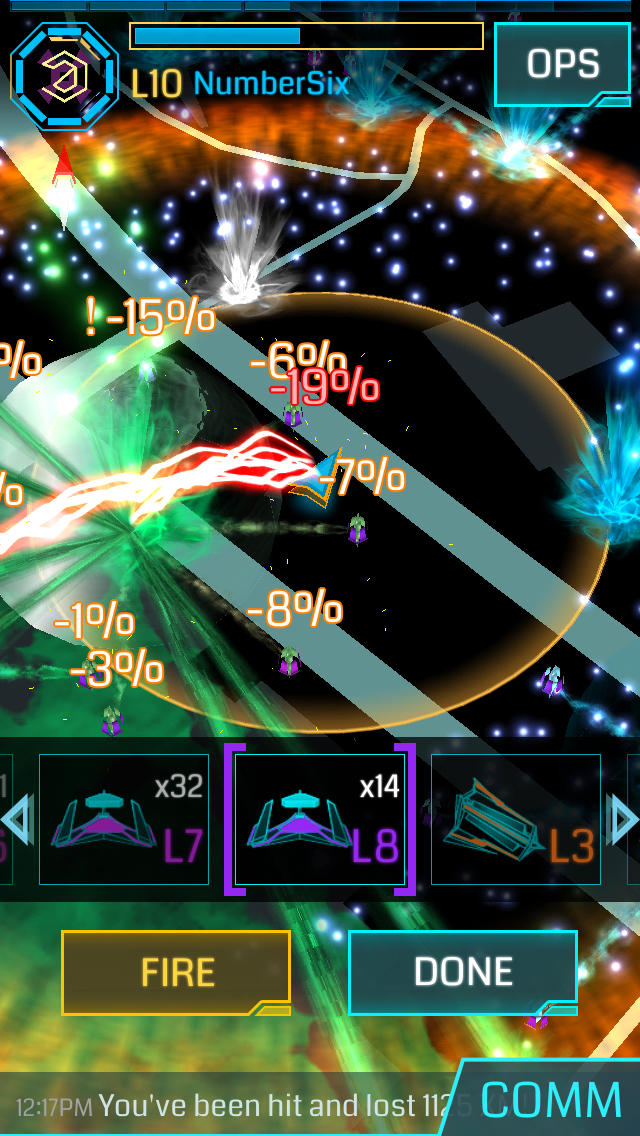
Earlier than Pokémon GO captivated tens of millions, Niantic, its developer, created Ingress, an AR sport that concerned gamers controlling digital portals overlaid on real-world places. Ingress served as an important testing floor and knowledge assortment software. Gamers, performing as subject brokers, explored their environments, submitting places for portals primarily based on factors of curiosity – historic markers, public artwork, distinctive buildings, and different vital landmarks. This large crowdsourced dataset turned the spine of Pokémon GO’s location-based options.
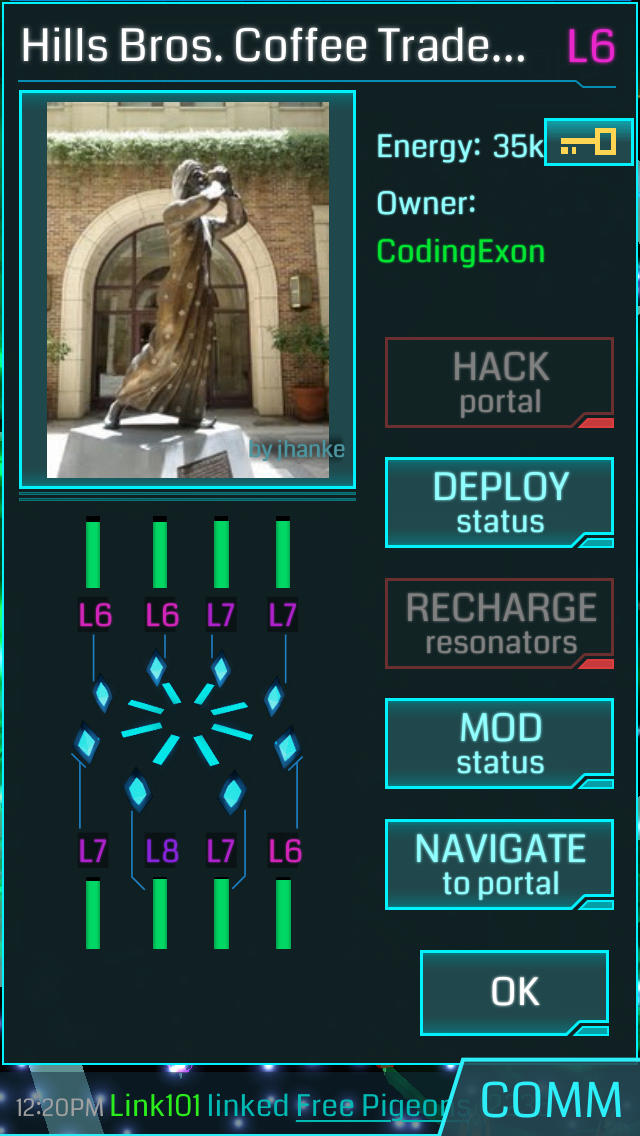
The Ingress knowledge wasn’t merely an inventory of coordinates; it contained wealthy contextual details about every location. This included descriptions, images, and player-submitted assessments of accessibility and suitability. This wealth of data proved invaluable in populating Pokémon GO’s world with PokéStops (primarily based on Ingress portals) and Gyms (typically strategically positioned round clusters of portals). The preliminary Pokémon GO map, subsequently, wasn’t constructed from scratch; it leveraged years of information painstakingly gathered by Ingress gamers.
This reliance on pre-existing knowledge considerably accelerated Pokémon GO’s improvement and launch. As an alternative of needing to create a very new map from scratch, Niantic may adapt and refine the prevailing Ingress infrastructure, saving appreciable time and assets. This additionally explains why sure places, significantly these with excessive concentrations of Ingress portals, typically have the next density of PokéStops and Gyms in Pokémon GO.
Past Ingress: OpenStreetMap and Different Knowledge Sources
Whereas Ingress shaped the core of Pokémon GO’s preliminary map knowledge, Niantic did not solely depend on it. OpenStreetMap (OSM), a collaborative, open-source map of the world, possible performed a supplementary function. OSM gives detailed details about roads, buildings, and different geographical options, which may have been used to reinforce the accuracy and completeness of the sport’s map. That is significantly related in areas the place Ingress had restricted participant protection.
Moreover, Niantic possible integrated knowledge from different sources, together with industrial mapping suppliers and authorities datasets. These further knowledge streams would have helped refine location accuracy, tackle inconsistencies, and make sure the sport’s map remained up-to-date. The method of integrating and harmonizing knowledge from various sources represents a major technical problem, requiring refined algorithms and knowledge processing methods.
The Dynamic Nature of the Pokémon GO Map
Not like static maps, the Pokémon GO map is dynamic and always evolving. New PokéStops and Gyms are added, present ones are modified or eliminated, and the sport’s underlying location knowledge is usually up to date. This dynamism is essential for sustaining participant engagement and reflecting real-world adjustments. For instance, if a brand new park opens, it is perhaps added to the sport as a location with elevated Pokémon spawns or new PokéStops. Conversely, if a constructing is demolished, the corresponding PokéStop or Fitness center is perhaps eliminated or relocated.
This ongoing upkeep requires a sturdy infrastructure and a steady suggestions loop. Niantic depends on participant reviews, neighborhood contributions, and its inside mapping groups to maintain the sport’s map correct and related. Gamers can submit recommendations for brand new PokéStops and Gyms, report errors in present places, and flag inappropriate content material. This neighborhood involvement is crucial to the sport’s success and ensures the map stays a fairly correct reflection of the actual world.
Google Maps’ Oblique Affect:
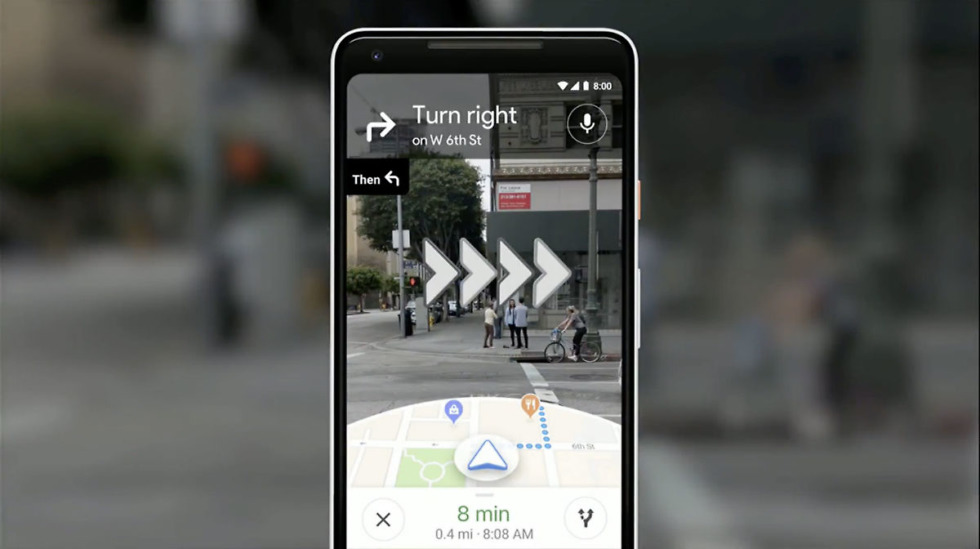
Whereas Pokémon GO does not straight make the most of Google Maps’ API for its main map show, Google Maps not directly influences the sport in a number of methods. Many gamers use Google Maps to navigate to PokéStops, Gyms, and areas with excessive Pokémon density. This complementary use highlights the interconnectedness of those mapping applied sciences inside the AR gaming ecosystem. Moreover, the underlying geographical knowledge utilized by Google Maps may need not directly influenced Niantic’s knowledge choice and validation processes. The accuracy and element of Google Maps in a selected area may have knowledgeable Niantic’s choices about which places to incorporate or exclude in Pokémon GO.
Challenges and Limitations:
Regardless of its sophistication, the Pokémon GO map faces a number of challenges. Sustaining accuracy throughout an enormous geographical space with always altering situations is a major endeavor. Knowledge discrepancies, inaccurate location info, and the necessity for ongoing upkeep signify ongoing hurdles. Moreover, the sport’s reliance on crowdsourced knowledge can result in biases, inconsistencies, and potential inaccuracies. Areas with restricted participant protection may need fewer PokéStops and Gyms in comparison with densely populated areas, resulting in an uneven distribution of sport options.
One other problem includes coping with personal property. The sport’s placement of PokéStops and Gyms on personal land has led to conflicts with landowners and raised privateness considerations. Niantic has carried out mechanisms to deal with these points, together with permitting gamers to report inappropriate places and implementing procedures for eradicating places from personal property.
The Way forward for Pokémon GO Mapping:
As AR know-how continues to evolve, the Pokémon GO map is more likely to turn out to be much more refined and built-in with real-world knowledge. The incorporation of extra superior mapping methods, equivalent to 3D modeling and real-time knowledge feeds, may improve the sport’s realism and immersive qualities. Using AI and machine studying may additionally enhance the accuracy and effectivity of information processing and site administration. Future iterations of the sport may even incorporate options that dynamically alter the map primarily based on real-time occasions, climate situations, or participant exercise.
In conclusion, the Pokémon GO map is a testomony to the ability of crowdsourced knowledge, the ingenuity of AR know-how, and the complicated interaction between digital and real-world areas. Whereas circuitously using Google Maps for its core map show, the sport’s success hinges on refined mapping applied sciences, leveraging the legacy of Ingress, OpenStreetMap, and different knowledge sources. The continued evolution of this map guarantees to additional blur the traces between the digital and bodily worlds, shaping the way forward for AR gaming and location-based leisure.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered worthwhile insights into Pokémon GO Map: Google Maps, Ingress, and the Augmented Actuality Panorama. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!