The Makeup-Acne Connection: Understanding Common Culprits And How To Avoid Breakouts
The Makeup-Acne Connection: Understanding Common Culprits and How to Avoid Breakouts
Related Articles: The Makeup-Acne Connection: Understanding Common Culprits and How to Avoid Breakouts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Makeup-Acne Connection: Understanding Common Culprits and How to Avoid Breakouts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Makeup-Acne Connection: Understanding Common Culprits and How to Avoid Breakouts
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While hormonal fluctuations and genetics play a significant role, external factors such as makeup can also contribute to breakouts. Understanding the specific makeup products that can trigger acne and learning how to mitigate their impact is crucial for maintaining clear skin.
Understanding the Mechanics of Makeup-Induced Acne
Acne develops when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. Makeup, particularly certain ingredients and formulations, can exacerbate this process. Here’s how:
-
Comedogenic Ingredients: These ingredients are known to clog pores, creating a breeding ground for acne-causing bacteria. Common comedogenic ingredients include:
- Oils: Mineral oil, coconut oil, and olive oil are often used in makeup products for their moisturizing properties. However, they can trap sebum and debris within pores, leading to breakouts.
- Waxes: Beeswax, carnauba wax, and candelilla wax are often used for texture and stability in makeup. While not inherently comedogenic, they can contribute to clogging if used in excessive amounts.
- Silicones: Silicones, such as dimethicone and cyclomethicone, are commonly found in primers, foundations, and concealers. They create a smooth, silky finish but can trap oil and debris, leading to breakouts in some individuals.
- Fatty Alcohols: These ingredients, such as cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, and cetearyl alcohol, are often used for their moisturizing and emulsifying properties. However, they can also contribute to pore blockage.
-
Improper Application and Removal: Applying excessive amounts of makeup or failing to remove it thoroughly can lead to clogged pores and subsequent acne. Makeup brushes and sponges can also harbor bacteria if not cleaned regularly, further contributing to breakouts.
-
Irritating Ingredients: Certain ingredients in makeup can irritate sensitive skin, triggering inflammation and acne. Common irritants include:
- Fragrances: Synthetic fragrances are often added to makeup for scent, but they can cause allergic reactions and inflammation in some individuals.
- Colorants: Certain dyes and pigments used in makeup can also irritate the skin.
- Preservatives: Preservatives are essential for extending the shelf life of makeup products, but some, such as parabens, can be irritating to sensitive skin.
Makeup Products Most Likely to Cause Acne
While any makeup product can potentially trigger acne, certain types are more notorious for their comedogenic properties:
-
Foundation: Foundations are applied directly to the skin and can contain high concentrations of comedogenic ingredients. Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic formulations specifically designed for acne-prone skin.
-
Concealer: Concealer is often used to cover blemishes, but it can also exacerbate them if it contains comedogenic ingredients. Choose oil-free, lightweight concealers that won’t clog pores.
-
Powder: Powders are designed to absorb oil and set makeup, but they can also clog pores if they contain ingredients like talc. Opt for loose powders formulated with mineral ingredients like silica and rice powder.
-
Primer: Primers are meant to create a smooth canvas for makeup application, but some contain silicones and other comedogenic ingredients. Look for oil-free, silicone-free primers specifically designed for acne-prone skin.
-
Mascara: Mascara can trap oil and bacteria on the lashes, leading to breakouts around the eyes. Choose oil-free, hypoallergenic mascaras and ensure you remove it thoroughly at the end of the day.
Tips for Preventing Makeup-Induced Acne
-
Choose Non-Comedogenic Products: Opt for makeup products labeled "non-comedogenic" or "oil-free." These products are formulated with ingredients less likely to clog pores.
-
Read Ingredient Lists: Familiarize yourself with common comedogenic ingredients and avoid products containing them.
-
Cleanse Thoroughly: Remove all makeup before bedtime using a gentle, oil-free cleanser.
-
Exfoliate Regularly: Exfoliating removes dead skin cells and prevents pore blockage. Use a gentle scrub or chemical exfoliant designed for acne-prone skin.
-
Keep Makeup Brushes and Sponges Clean: Wash your makeup brushes and sponges regularly with a gentle cleanser to prevent bacteria buildup.
-
Limit Makeup Use: If possible, reduce the amount of makeup you wear, particularly during hot and humid weather.
-
Patch Test New Products: Before using a new makeup product, test it on a small area of skin to check for any allergic reactions or irritation.
-
Consult a Dermatologist: If you experience persistent acne despite following these tips, consult a dermatologist for personalized advice and treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is it okay to wear makeup if I have acne-prone skin?
A: Yes, it is okay to wear makeup even if you have acne-prone skin. However, it’s essential to choose products formulated for sensitive skin and to follow proper application and removal techniques.
Q: How can I tell if a makeup product is comedogenic?
A: Look for products labeled "non-comedogenic" or "oil-free." You can also research the ingredients list and avoid products containing known comedogenic ingredients.
Q: How often should I clean my makeup brushes and sponges?
A: Ideally, you should clean your makeup brushes and sponges weekly. However, if you use them daily, you may need to clean them more frequently.
Q: Can certain types of makeup be more likely to cause acne than others?
A: Yes, certain types of makeup, such as foundation, concealer, and powder, are more likely to cause acne due to their potential to clog pores.
Q: What are some natural alternatives to makeup products that can cause acne?
A: There are many natural alternatives to makeup products that can cause acne. For example, you can use mineral makeup, which is typically non-comedogenic and hypoallergenic. You can also use natural ingredients like aloe vera and tea tree oil to treat acne and soothe irritated skin.
Conclusion
While makeup can enhance one’s appearance, it’s crucial to be mindful of its potential impact on acne. By understanding the common culprits, following proper application and removal techniques, and choosing non-comedogenic products, individuals can minimize the risk of makeup-induced breakouts and maintain clear, healthy skin. Remember, if you experience persistent acne, seeking professional advice from a dermatologist is always recommended.
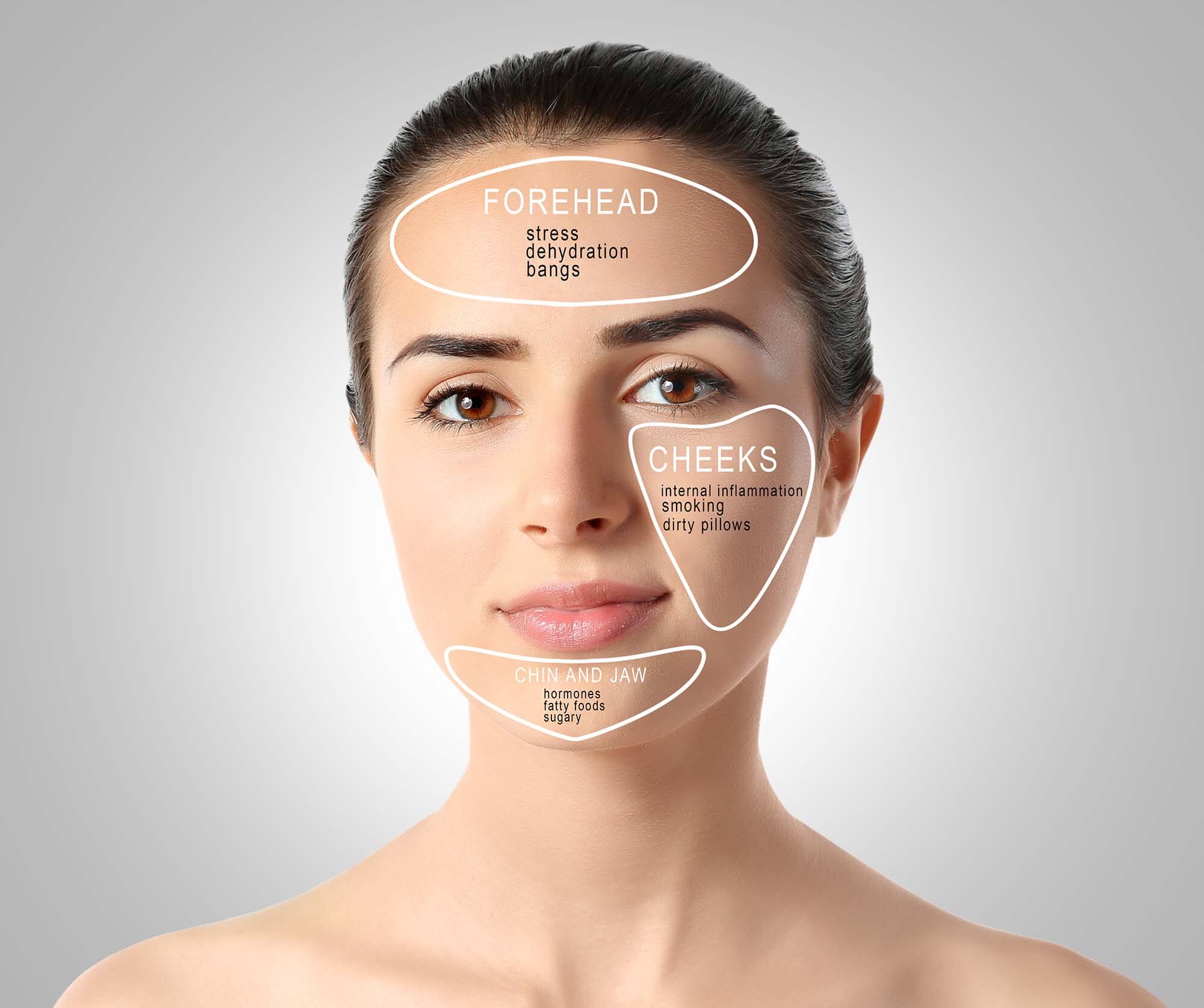








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Makeup-Acne Connection: Understanding Common Culprits and How to Avoid Breakouts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!